NEFM DNA methylation correlates with immune infiltration and survival in breast cancer
- PMID: 34001208
- PMCID: PMC8130356
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-021-01096-4
NEFM DNA methylation correlates with immune infiltration and survival in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: This study aims to determine whether NEFM (neurofilament medium) DNA methylation correlates with immune infiltration and prognosis in breast cancer (BRCA) and to explore NEFM-connected immune gene signature.
Methods: NEFM transcriptional expression was analyzed in BRCA and normal breast tissues using Oncomine and Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) databases. The relationship between NEFM DNA methylation and NEFM transcriptional expression was investigated in TCGA. Potential influence of NEFM DNA methylation/expression on clinical outcome was evaluated using TCGA BRCA, The Human Protein Atlas and Kaplan-Meier plotter databases. Association of NEFM transcriptional expression/DNA methylation with cancer immune infiltration was investigated using TIMER and TISIDB databases.
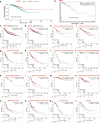
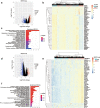
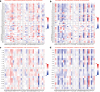
Results: High expression of NEFM correlated with better overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in TCGA BRCA and Kaplan-Meier plotter, whereas NEFM DNA methylation with worse OS in TCGA BRCA. NEFM transcriptional expression negatively correlated with DNA methylation. NEFM DNA methylation significantly negatively correlated with infiltrating levels of B, CD8+ T/CD4+ T cells, macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells in TIMER and TISIDB. NEFM expression positively correlated with macrophage infiltration in TIMER and TISIDB. After adjusted with tumor purity, NEFM expression weekly negatively correlated with infiltration level of B cells, whereas positively correlated with CD8+ T cell infiltration in TIMER gene modules. NEFM expression/DNA methylation correlated with diverse immune markers in TCGA and TISIDB.
Conclusions: NEFM low-expression/DNA methylation correlates with poor prognosis. NEFM expression positively correlates with macrophage infiltration. NEFM DNA methylation strongly negatively correlates with immune infiltration in BRCA. Our study highlights novel potential functions of NEFM expression/DNA methylation in regulation of tumor immune microenvironment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; DNA methylation; Lymphocytes; NEFM; Prognosis; Tumor-infiltrating.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High expression of eIF4E is associated with tumor macrophage infiltration and leads to poor prognosis in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Dec 7;21(1):1305. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09010-0. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34876062 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation study of PBK/TOPK expression, prognosis, and immune infiltration in breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 29;15(1):15052. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96542-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40301429 Free PMC article.
-
Ceruloplasmin correlates with immune infiltration and serves as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Aug 19;13(16):20438-20467. doi: 10.18632/aging.203427. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34413268 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Biomarkers of Breast Cancer Risk: Across the Breast Cancer Prevention Continuum.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;882:33-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22909-6_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26987530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic role of EGR1 in breast cancer: a systematic review.BMB Rep. 2021 Oct;54(10):497-504. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.10.087. BMB Rep. 2021. PMID: 34488929 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
APOB is a potential prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2024 Feb 3;15(1):28. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-00877-6. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38310202 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modification in radiotherapy and immunotherapy for cancers.Tzu Chi Med J. 2024 Sep 5;36(4):396-406. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_3_24. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. Tzu Chi Med J. 2024. PMID: 39421493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Novel Gene Signature with DDR and EMT Difunctionalities for Predicting Prognosis, Immune Activity, and Drug Response in Breast Cancer.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 10;20(2):1221. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021221. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673982 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting DNA Methylation Machinery in Pediatric Solid Tumors.Cells. 2024 Jul 18;13(14):1209. doi: 10.3390/cells13141209. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39056791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Prognostic Relevance of Differential Claudin Gene Expression Highlights Claudin-4 as Being Suppressed by TGFβ1 Inhibitor in Colorectal Cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Feb 24;13:783016. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.783016. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35281827 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

