Orthostatic hypotension in older people: considerations, diagnosis and management
- PMID: 34001585
- PMCID: PMC8140709
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-1044
Orthostatic hypotension in older people: considerations, diagnosis and management
Abstract
Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is very common in older people and is encountered daily in emergency departments and medical admissions units. It is associated with a higher risk of falls, fractures, dementia and death, so prompt recognition and treatment are essential. In this review article, we describe the physiology of standing (orthostasis) and the pathophysiology of orthostatic hypotension. We focus particularly on aspects pertinent to older people. We review the evidence and consensus management guidelines for all aspects of management. We also tackle the challenge of concomitant orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension, providing a treatment overview as well as practical suggestions for management. In summary, orthostatic hypotension (and associated supine hypertension) are common, dangerous and disabling, but adherence to simple structures management strategies can result in major improvements.
Keywords: older; orthostasis; orthostatic hypotension; postural hypotension; supine hypertension.
© Royal College of Physicians 2021. All rights reserved.
Figures
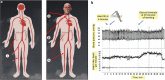
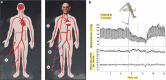
References
-
- Lahrmann H, Cortelli P, Hilz M, et al. EFNS guidelines on the diagnosis and management of orthostatic hypotension. Eur J Neurol 2006;13:930–6. - PubMed
-
- Sarasin FP, Louis-Simonet M, Carballo D, et al. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension among patients presenting with syncope in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 2002;20:497–501. - PubMed
-
- Ricci F, Fedorowski A, Radico F, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality related to orthostatic hypotension: a meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Eur Heart J 2015;36:1609–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

