Diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD: an individual patient data meta-analysis
- PMID: 34001645
- PMCID: PMC8995830
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324243
Diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD: an individual patient data meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Liver biopsy is still needed for fibrosis staging in many patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The aims of this study were to evaluate the individual diagnostic performance of liver stiffness measurement by vibration controlled transient elastography (LSM-VCTE), Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4) and NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) Fibrosis Score (NFS) and to derive diagnostic strategies that could reduce the need for liver biopsies.
Design: Individual patient data meta-analysis of studies evaluating LSM-VCTE against liver histology was conducted. FIB-4 and NFS were computed where possible. Sensitivity, specificity and area under the receiver operating curve (AUROC) were calculated. Biomarkers were assessed individually and in sequential combinations.
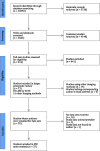
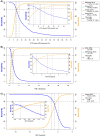
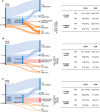
Results: Data were included from 37 primary studies (n=5735; 45% women; median age: 54 years; median body mass index: 30 kg/m2; 33% had type 2 diabetes; 30% had advanced fibrosis). AUROCs of individual LSM-VCTE, FIB-4 and NFS for advanced fibrosis were 0.85, 0.76 and 0.73. Sequential combination of FIB-4 cut-offs (<1.3; ≥2.67) followed by LSM-VCTE cut-offs (<8.0; ≥10.0 kPa) to rule-in or rule-out advanced fibrosis had sensitivity and specificity (95% CI) of 66% (63-68) and 86% (84-87) with 33% needing a biopsy to establish a final diagnosis. FIB-4 cut-offs (<1.3; ≥3.48) followed by LSM cut-offs (<8.0; ≥20.0 kPa) to rule out advanced fibrosis or rule in cirrhosis had a sensitivity of 38% (37-39) and specificity of 90% (89-91) with 19% needing biopsy.
Conclusion: Sequential combinations of markers with a lower cut-off to rule-out advanced fibrosis and a higher cut-off to rule-in cirrhosis can reduce the need for liver biopsies.
Keywords: biostatistics; clinical decision making; fatty liver; hepatic fibrosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AG reports personal fees from AbbVie, personal fees from Alexion, personal fees from Bayer, personal fees from BMS, personal fees from CSL Behring, personal fees from Gilead, grants and personal fees from Intercept, personal fees from Ipsen, personal fees from Merz, grants and personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Sanofi-Aventis, personal fees from Sequana, grants and personal fees from Falk, personal fees from MSD, during the conduct of the study. ANAJ reports other from Perspectum, during the conduct of the study. CF reports other from Echosens, during the conduct of the study. JFC reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, personal fees from Novo Nordisk, personal fees from Intercept, personal fees from Alnylam, during the conduct of the study. JB reports other from Pfizer, during the conduct of the study. JMS reports personal fees from BMS, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from Echosens, personal fees from Genfit, personal fees from Gilead Sciences, personal fees from Intercept Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Madrigal, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Roche, personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Falk Foundation, personal fees from MSD, grants from Gilead Sciences, during the conduct of the study. JW reports grants from Echosens, during the conduct of the study. Dr. Pavlides reports other from Perspectum, during the conduct of the study. MT reports personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Falk Foundation, personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from Intercept, personal fees from Merck Sharp & Dohme, personal fees from Albireo, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from BiomX, personal fees from Falk Pharma GmbH, personal fees from GENFIT, personal fees from Jannsen, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Phenex, personal fees from Regulus and Shire, grants from AbbVie, grants from Falk, grants from Gilead, grants from Intercept, grants from Albireo, grants from CymaBay, grants from Merck Sharp & Dohme, grants from Takeda, during the conduct of the study; in addition, MT has a patent norUDCA issued. PNN reports personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Novo Nordisk, personal fees from Poxel, grants from Pharmaxis, grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, grants from Echosens, grants from Novo Nordisk, during the conduct of the study. QMA reports grants from AbbVie, grants and personal fees from Allergan/Tobira, grants from AstraZeneca, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants from Glympse Bio, grants and personal fees from Novartis Pharma, grants and personal fees from Pfizer, grants from Vertex, personal fees from Abbott Laboratories, personal fees from Acuitas Medical, personal fees from Blade, personal fees from BNN Cardio, personal fees from Cirius, personal fees from CymaBay, personal fees from EcoR1, personal fees from Eli Lilly, personal fees from Galmed, personal fees from Genfit, personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from Grunthal, personal fees from HistoIndex, personal fees from Indalo, personal fees from Imperial Innovations, personal fees from Intercept Pharma Europe, personal fees from Inventiva, personal fees from IQVIA, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Kenes, personal fees from Madrigal, personal fees from MedImmune, personal fees from Metacrine, personal fees from NewGene, personal fees from NGMBio, personal fees from North Sea Therapeutics, personal fees from Novo Nordisk, personal fees from Poxel, personal fees from ProSciento, personal fees from Raptor Pharma, personal fees from Servier, personal fees from Viking Therapeutics, personal fees from Abbott Laboratories, personal fees from BMS, personal fees from Clinical Care Options, personal fees from Falk, personal fees from Fishawack, personal fees from Integritas Communications, personal fees from MedScape, other from IMI2 LITMUS consortium, during the conduct of the study. SH reports grants and personal fees from Akero, grants and personal fees from Axcella, grants and personal fees from Cirius, grants and personal fees from CiVi Biopharma, grants and personal fees from CymaBay, grants and personal fees from Galectin, grants from Galmed, grants and personal fees from Genfit, grants and personal fees from Gilead Sciences, grants and personal fees from Hepion Pharmaceuticals, grants and personal fees from Hightide Therapeutics, grants and personal fees from Intercept, grants and personal fees from Madrigal, grants and personal fees from Metacrine, grants and personal fees from NGM Bio, grants and personal fees from North Sea Therapeutics, grants and personal fees from Novartis, grants and personal fees from Novo Nordisk, grants and personal fees from Poxel, grants and personal fees from Sagimet, grants and personal fees from Viking, personal fees from Altimmune, personal fees from Alentis, personal fees from Arrowhead, personal fees from Canfite, personal fees from Echosens, personal fees from Enyo, personal fees from Fibronostics, personal fees from Foresite Labs, personal fees from Fortress Biotech, personal fees from HistoIndex, personal fees from Kowa, personal fees from Prometic, personal fees from Ridgeline, personal fees from Terns, during the conduct of the study. SM reports personal fees from Echosens, during the conduct of the study. SN reports other from Perspectum, during the conduct of the study. SP reports personal fees from AbbVie, personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from Intercept, personal fees from Pfizer, during the conduct of the study. TK reports grants from Echosens, during the conduct of the study. TT reports other from Pfizer, during the conduct of the study. VdL reports personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Gilead Sciences, personal fees from AbbVie, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Echosens, personal fees from Intercept Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from MSD, personal fees from Myr-Pharma, personal fees from Supersonic Imagine, personal fees from Tillotts, during the conduct of the study. Dr. Wong reports personal fees from AbbVie, personal fees from 3V-BIO, personal fees from Allergan, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from Center for Outcomes Research in Liver Diseases, grants and personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from Intercept, personal fees from Echosens, personal fees from Hanmi Pharmaceutical, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Merck, personal fees from Novo Nordisk, personal fees from Perspectum, personal fees from ProSciento, personal fees from Sagimet Biosciences, personal fees from TARGET PharmaSolutions, personal fees from Terns, personal fees from BMS, during the conduct of the study. WK reports personal fees from Samil, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from Ildong, personal fees from LG Chemistry, personal fees from Gilead Sciences, personal fees from HK inno.N, personal fees from GreenCross, personal fees from Bukwang, personal fees from Standigm, personal fees from PharmaKing, personal fees from KOBIOLABS, personal fees from Eisai, personal fees from Zydus, personal fees from Novo Nordisk, grants from Gilead, grants from Ildong, grants from GreenCross, grants from Bukwang, grants from PharmaKing, grants from Roche, grants from Galmed, grants from Novartis, grants from Pfizer, grants from Springbank, grants from Altimmune, grants from MSD, grants from BMS, grants from Dicerna, grants from Enyo, grants from Hitachi-Aloka, other from KOBIOLABS, other from Lepidyne, during the conduct of the study. YY reports grants from Biocodes, grants and personal fees from Gilead Sciences, personal fees from Bilim Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Pharmactive Pharmaceutical, personal fees from Sanovel Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Galmed, personal fees from Zydus, personal fees from Novo Nordisk, during the conduct of the study. MP, ANAJ and SN are shareholders of Perspectum, Oxford, UK. CF is employed by Echosens, France. MT received speaker fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), Falk Foundation, Gilead, Intercept and Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD); advisory board fees from Albireo, Boehringer Ingelheim, BiomX, Falk Pharma GmbH, GENFIT, Gilead, Intercept, Jannsen, MSD, Novartis, Phenex, Regulus and Shire; travel grants from AbbVie, Falk, Gilead, and Intercept; and research grants from Albireo, CymaBay, Falk, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, and Takeda. He is also coinventor of patents on the medical use of norUDCA filed by the Medical University of Graz. SP was speaker and/or Advisor for AbbVie, Gilead, Intercept and Pfizer. PNN received grant and research support from Pharmaxis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Echosens and Novo Nordisk and consulting fees from BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Poxel on behalf of the University of Birmingham. VL reports consultancy for AbbVie, BMS, Echosens, Gilead Sciences, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, MSD, Myr-Pharma, Pfizer, Supersonic Imagine and Tillotts. SM received honorarium fees from Echosens. JFC received consultancy, advisory board, and speaker fees from Astra Zeneca, NovoNordisk, Intercept and Alnylam. JMS reports consultancy for BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Madrigal, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi; received research funding from Gilead Sciences and was on the speakers bureau for Falk Foundation MSD Sharp & Dohme GmbH. WK has served as a speaker and consultant of Gilead, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Samil, Ildong, LG Chemistry, HK inno.N, GreenCross, Bukwang, Standigm, PharmaKing, KOBIOLABS, Eisai, Zydus, and Novonordisk, received grants from Gilead, Ildong, GreenCross, Bukwang, Pharmaking, Roche, Galmed, Novartis, Pfizer, Springbank, Altimmune, MSD, BMS, Dicerna, Enyo, and Hitachi-Aloka, and owns stocks in KOBIOLABS and Lepidyne. TK and JW received unrestricted research grants from Echosens, Paris France. TK participated in a clinical advisory board meeting. YY received research grant from Biocodex, Gilead Sciences, speaker fees for Gilead Sciences, Bilim Pharmaceuticals, Pharmactive Pharmaceutical, Sanovel Pharmaceuticals, and served as advisory board member for Galmed, Zydus, NovoNordisk. AG reports consultancy for AbbVie, Alexion, Bayer, BMS, CSL Behring, Gilead, Intercept, Ipsen, Merz, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, Sequana; received research funding from Intercept, Falk, Novartis and was on the speakers bureau for AbbVie, Alexion, BMS, CSL Behring, Falk Foundation, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, Merz, Novartis, Sequana. VWSW has served as a consultant or advisory board member for 3V-BIO, AbbVie, Allergan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Center for Outcomes Research in Liver Diseases, Echosens, Gilead Sciences, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, Intercept, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Perspectum Diagnostics, Pfizer, ProSciento, Sagimet Biosciences, TARGET PharmaSolutions, and Terns; and a speaker for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Echosens, and Gilead Sciences. He has also received a research grant from Gilead Sciences for fatty liver research. QMA is coordinator of the IMI2 LITMUS consortium and he reports research grant funding from Abbvie, Allergan/Tobira, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Glympse Bio, Novartis Pharma AG, Pfizer Ltd., Vertex; consultancy on behalf of Newcastle University for Abbott Laboratories, Acuitas Medical, Allergan/Tobira, Blade, BNN Cardio, Cirius, CymaBay, EcoR1, E3Bio, Eli Lilly & Company Ltd., Galmed, Genfit SA, Gilead, Grunthal, HistoIndex, Indalo, Imperial Innovations, Intercept Pharma Europe Ltd., Inventiva, IQVIA, Janssen, Kenes, Madrigal, MedImmune, Metacrine, NewGene, NGMBio, North Sea Therapeutics, Novartis, Novo Nordisk A/S, Pfizer Ltd., Poxel, ProSciento, Raptor Pharma, Servier, Viking Therapeutics; and speaker fees from Abbott Laboratories, Allergan/Tobira, BMS, Clinical Care Options, Falk, Fishawack, Genfit SA, Gilead, Integritas Communications, MedScape. SAH has research grants from Akero, Axcella, Cirius, CiVi Biopharma, Cymabay, Galectin, Galmed, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Hepion Pharmaceuticals, Hightide Therapeutics, Intercept, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM Bio, Northsea Therapeutics, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Poxel, Sagimet, Viking. He has received consulting fees from Akero, Altimmune, Alentis, Arrowhead, Axcella, Canfite, Cirius, CiVi, Cymabay, Echosens, Enyo, Fibronostics, Foresite Labs, Fortress Biotech, Galectin, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Hepion, HIghtide, HistoIndex, Intercept, Kowa, Madrigal, Metacrine, NGM, Northsea, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Poxel, Prometic, Ridgeline, Sagimet, Terns, and Viking.
Figures
Comment in
-
Non-invasive tests and advanced chronic liver disease in NAFLD: two steps forward and one step back?Gut. 2022 Jun;71(6):1236-1237. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325994. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Gut. 2022. PMID: 34521766 No abstract available.
References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) . EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes Facts 2016;9:65–90. 10.1159/000443344 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
