Safety and efficacy of meplazumab in healthy volunteers and COVID-19 patients: a randomized phase 1 and an exploratory phase 2 trial
- PMID: 34001849
- PMCID: PMC8127508
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00603-6
Safety and efficacy of meplazumab in healthy volunteers and COVID-19 patients: a randomized phase 1 and an exploratory phase 2 trial
Abstract
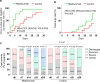
Recent evidence suggests that CD147 serves as a novel receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Blocking CD147 via anti-CD147 antibody could suppress the in vitro SARS-CoV-2 replication. Meplazumab is a humanized anti-CD147 IgG2 monoclonal antibody, which may effectively prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Here, we conducted a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of meplazumab in healthy subjects, and an open-labeled, concurrent controlled add-on exploratory phase 2 study to determine the efficacy in COVID-19 patients. In phase 1 study, 59 subjects were enrolled and assigned to eight cohorts, and no serious treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) or TEAE grade ≥3 was observed. The serum and peripheral blood Cmax and area under the curve showed non-linear pharmacokinetic characteristics. No obvious relation between the incidence or titer of positive anti-drug antibody and dosage was observed in each cohort. The biodistribution study indicated that meplazumab reached lung tissue and maintained >14 days stable with the lung tissue/cardiac blood-pool ratio ranging from 0.41 to 0.32. In the exploratory phase 2 study, 17 COVID-19 patients were enrolled, and 11 hospitalized patients were involved as concurrent control. The meplazumab treatment significantly improved the discharged (P = 0.005) and case severity (P = 0.021), and reduced the time to virus negative (P = 0.045) in comparison to the control group. These results show a sound safety and tolerance of meplazumab in healthy volunteers and suggest that meplazumab could accelerate the recovery of patients from COVID-19 pneumonia with a favorable safety profile.
Conflict of interest statement
P.Z., Z.-N.C., H.B., and Z.Z. were the inventors of the patent Humanized anti-basigin antibodies and the use thereof (PCT/CN2017/082713), and all of the above authors were not the applicant or patentee of the patent. P.Z., Z.-N.C., H.B., D.W., and Z.Z. were the inventors of patent Humanized anti-basigin antibody for use of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) therapy (202010166717.9, China), and all of the above authors were not the applicant or patentee of the patent. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology, T. The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi41, 145–151 (2020). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization.Clinical Management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection when Novel Coronavirus (nCoV) Infection is Suspected,Vol. WHO/nCoV/Clinical/2020.3 (WHO, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

