A universal strategy towards high-energy aqueous multivalent-ion batteries
- PMID: 34001901
- PMCID: PMC8128864
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23209-6
A universal strategy towards high-energy aqueous multivalent-ion batteries
Abstract
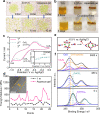
Rechargeable multivalent metal (e.g., Ca, Mg or, Al) batteries are ideal candidates for large-scale electrochemical energy storage due to their intrinsic low cost. However, their practical application is hampered by the low electrochemical reversibility, dendrite growth at the metal anodes, sluggish multivalent-ion kinetics in metal oxide cathodes and, poor electrode compatibility with non-aqueous organic-based electrolytes. To circumvent these issues, here we report various aqueous multivalent-ion batteries comprising of concentrated aqueous gel electrolytes, sulfur-containing anodes and, high-voltage metal oxide cathodes as alternative systems to the non-aqueous multivalent metal batteries. This rationally designed aqueous battery chemistry enables satisfactory specific energy, favorable reversibility and improved safety. As a demonstration model, we report a room-temperature calcium-ion/sulfur| |metal oxide full cell with a specific energy of 110 Wh kg-1 and remarkable cycling stability. Molecular dynamics modeling and experimental investigations reveal that the side reactions could be significantly restrained through the suppressed water activity and formation of a protective inorganic solid electrolyte interphase. The unique redox chemistry of the multivalent-ion system is also demonstrated for aqueous magnesium-ion/sulfur||metal oxide and aluminum-ion/sulfur||metal oxide full cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Jiang L, et al. Building aqueous K–ion batteries for energy storage. Nat. Energy. 2019;4:495–503. doi: 10.1038/s41560-019-0388-0. - DOI
-
- Li M, et al. Design strategies for nonaqueous multivalent–ion and monovalent–ion battery anodes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020;5:276–294. doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0166-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

