Polymer-free corticosteroid dimer implants for controlled and sustained drug delivery
- PMID: 34001908
- PMCID: PMC8129133
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23232-7
Polymer-free corticosteroid dimer implants for controlled and sustained drug delivery
Abstract
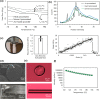
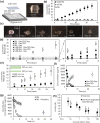
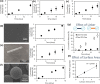
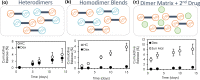
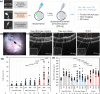
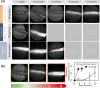
Polymeric drug carriers are widely used for providing temporal and/or spatial control of drug delivery, with corticosteroids being one class of drugs that have benefitted from their use for the treatment of inflammatory-mediated conditions. However, these polymer-based systems often have limited drug-loading capacity, suboptimal release kinetics, and/or promote adverse inflammatory responses. This manuscript investigates and describes a strategy for achieving controlled delivery of corticosteroids, based on a discovery that low molecular weight corticosteroid dimers can be processed into drug delivery implant materials using a broad range of established fabrication methods, without the use of polymers or excipients. These implants undergo surface erosion, achieving tightly controlled and reproducible drug release kinetics in vitro. As an example, when used as ocular implants in rats, a dexamethasone dimer implant is shown to effectively inhibit inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide. In a rabbit model, dexamethasone dimer intravitreal implants demonstrate predictable pharmacokinetics and significantly extend drug release duration and efficacy (>6 months) compared to a leading commercial polymeric dexamethasone-releasing implant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: K.B., I.P., M.A.J.S., D.L., G.M., H.F., A.D., E.B., B.Y., J.P.S., and W.N. are employees of Ripple Therapeutics. F.G. is a former employee of Ripple Therapeutics. Ripple Therapeutics has a financial interest in the materials presented in this publication. As employees of Ripple Therapeutics, K.B., I.P., M.A.J.S., D.L., G.M., H.F., A.D., E.B., B.Y., J.P.S., and W.N. have a financial interest in the company in the form of shares and some employees are authors on patents related to the materials in this manuscript (K.B., I.P., M.A.J.S., D.L., H.F., A.D., J.P.S., W.N.). L.K., J.E., and C.C. receive remuneration for consultation from Ripple Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

