Cytokine release syndrome and associated neurotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 34002066
- PMCID: PMC8127450
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-021-00547-6
Cytokine release syndrome and associated neurotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
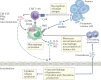
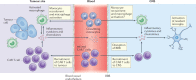
A paradigm shift has recently occurred in the field of cancer therapeutics. Traditional anticancer agents, such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy and small-molecule drugs targeting specific signalling pathways, have been joined by cellular immunotherapies based on T cell engineering. The rapid adoption of novel, patient-specific cellular therapies builds on scientific developments in tumour immunology, genetic engineering and cell manufacturing, best illustrated by the curative potential of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy targeting CD19-expressing malignancies. However, the clinical benefit observed in many patients may come at a cost. In up to one-third of patients, significant toxicities occur that are directly associated with the induction of powerful immune effector responses. The most frequently observed immune-mediated toxicities are cytokine release syndrome and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome. This Review discusses our current understanding of their pathophysiology and clinical features, as well as the development of novel therapeutics for their prevention and/or management.
© 2021. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
M.S. and T.G. are listed as inventors in a Memorial Sloan Kettering-held patent application related to treatment of cytokine release syndrome: ‘Methods and compositions for alleviating cytokine release syndrome’ (WO2019099993A1). E.C.M. is scientific co-founder of Quell Therapeutics Ltd, which is developing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified regulatory T cells, and has served as a consultant to Kite, a Gilead company. S.S.N. served as consultant to Kite, a Gilead Company, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Celgene, Pfizer, Allogene Therapeutics, Cell Medica/Kuur, Incyte, Precision Biosciences, Legend Biotech, Adicet Bio, Calibr and Unum Therapeutics; received research support from Kite, a Gilead Company, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Poseida, Cellectis, Celgene, Karus Therapeutics, Unum Therapeutics, Allogene Therapeutics, Precision Biosciences and Acerta; received royalties from Takeda Pharmaceuticals; and has intellectual property related to cell therapy.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

