A fractional order Covid-19 epidemic model with Mittag-Leffler kernel
- PMID: 34002105
- PMCID: PMC8114791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111030
A fractional order Covid-19 epidemic model with Mittag-Leffler kernel
Abstract
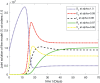
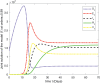
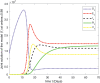
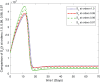
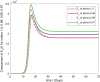
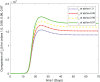
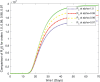
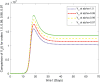
In this article, we are studying fractional-order COVID-19 model for the analytical and computational aspects. The model consists of five compartments including; which denotes susceptible class, represents exposed population, is the class for infected people who have been developed with COVID-19 and can cause spread in the population. The recovered class is denoted by and is the concentration of COVID-19 virus in the area. The computational study shows us that the spread will be continued for long time and the recovery reduces the infection rate. The numerical scheme is based on the Lagrange's interpolation polynomial and the numerical results for the suggested model are similar to the integer order which gives us the applicability of the numerical scheme and effectiveness of the fractional order derivative.
Keywords: 35R11; Primary 26A33; Secondary 34A08.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
On a comprehensive model of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) under Mittag-Leffler derivative.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020 Jun;135:109867. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109867. Epub 2020 May 8. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020. PMID: 32390692 Free PMC article.
-
A fuzzy fractional model of coronavirus (COVID-19) and its study with Legendre spectral method.Results Phys. 2021 Feb;21:103773. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103773. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Results Phys. 2021. PMID: 33391986 Free PMC article.
-
On modified Mittag-Leffler coupled hybrid fractional system constrained by Dhage hybrid fixed point in Banach algebra.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 4;14(1):30264. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81568-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39632896 Free PMC article.
-
Why the Mittag-Leffler Function Can Be Considered the Queen Function of the Fractional Calculus?Entropy (Basel). 2020 Nov 30;22(12):1359. doi: 10.3390/e22121359. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33266284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of fractional epidemic models.Appl Math Model. 2021 Sep;97:281-307. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2021.03.044. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Appl Math Model. 2021. PMID: 33897091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stability analysis and solutions of fractional boundary value problem on the cyclopentasilane graph.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 10;10(12):e32411. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32411. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38975069 Free PMC article.
-
Application of piecewise fractional differential equation to COVID-19 infection dynamics.Results Phys. 2022 Aug;39:105685. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105685. Epub 2022 Jun 4. Results Phys. 2022. PMID: 35694036 Free PMC article.
-
A vigorous study of fractional order COVID-19 model via ABC derivatives.Results Phys. 2021 Oct;29:104737. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104737. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Results Phys. 2021. PMID: 34485028 Free PMC article.
-
The role of a vaccine booster for a fractional order model of the dynamic of COVID-19: a case study in Thailand.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 7;15(1):1162. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80390-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39774616 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the dynamics of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) via stochastic epidemic model.Results Phys. 2021 May;24:104004. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104004. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Results Phys. 2021. PMID: 33816091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Novel coronavirus-China. 2020. URL: https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en.
-
- World Health Organization . situation report, 72. 2019. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
-
- Ming W.K., Huang J., Zhang C.J. Breaking down of healthcare system: mathematical modelling for controlling the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak in Wuhan, China. bioRxiv. 2020
-
Jan 1
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

