Admission Urinary and Serum Metabolites Predict Renal Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients With Cirrhosis
- PMID: 34002868
- PMCID: PMC9338693
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.31907
Admission Urinary and Serum Metabolites Predict Renal Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients With Cirrhosis
Abstract
Background and aims: Acute kidney injury (AKI) has a poor prognosis in cirrhosis. Given the variability of creatinine, the prediction of AKI and dialysis by other markers is needed. The aim of this study is to determine the role of serum and urine metabolomics in the prediction of AKI and dialysis in an inpatient cirrhosis cohort.
Approach and results: Inpatients with cirrhosis from 11 North American Consortium of End-stage Liver Disease centers who provided admission serum/urine when they were AKI and dialysis-free were included. Analysis of covariance adjusted for demographics, infection, and cirrhosis severity was performed to identify metabolites that differed among patients (1) who developed AKI or not; (2) required dialysis or not; and/pr (3) within AKI subgroups who needed dialysis or not. We performed random forest and AUC analyses to identify specific metabolite(s) associated with outcomes. Logistic regression with clinical variables with/without metabolites was performed. A total of 602 patients gave serum (218 developed AKI, 80 needed dialysis) and 435 gave urine (164 developed AKI, 61 needed dialysis). For AKI prediction, clinical factor-adjusted AUC was 0.91 for serum and 0.88 for urine. Major metabolites such as uremic toxins (2,3-dihydroxy-5-methylthio-4-pentenoic acid [DMTPA], N2N2dimethylguanosine, uridine/pseudouridine) and tryptophan/tyrosine metabolites (kynunerate, 8-methoxykyunerate, quinolinate) were higher in patients who developed AKI. For dialysis prediction, clinical factor-adjusted AUC was 0.93 for serum and 0.91 for urine. Similar metabolites as AKI were altered here. For dialysis prediction in those with AKI, the AUC was 0.81 and 0.79 for serum/urine. Lower branched-chain amino-acid (BCAA) metabolites but higher cysteine, tryptophan, glutamate, and DMTPA were seen in patients with AKI needing dialysis. Serum/urine metabolites were additive to clinical variables for all outcomes.
Conclusions: Specific admission urinary and serum metabolites were significantly additive to clinical variables to predict AKI development and dialysis initiation in inpatients with cirrhosis. These observations can potentially facilitate earlier initiation of renoprotective measures.
© 2021 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Dr. Reddy advises and received grants from Mallinckrodt. He received grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Merck, Intercept, Sequana, Grifols, and Exact Sciences. Dr. O’Leary is on the speakers’ bureau for Gilead and AbbVie.
Figures


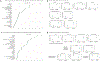
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor: Biomarkers for Predicting Renal Outcomes in Decompensated Cirrhosis: Need a Closer Look!Hepatology. 2021 Nov;74(5):2915-2916. doi: 10.1002/hep.32005. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 34107074 No abstract available.
-
REPLY.Hepatology. 2021 Nov;74(5):2916-2917. doi: 10.1002/hep.32006. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 34110034 No abstract available.
References
-
- Angeli P, Ginès P, Wong F, Bernardi M, Boyer TD, Gerbes A, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. J Hepatol 2015;62:968–974. - PubMed
-
- Wong F, Murray P. Kidney damage biomarkers: Novel tools for the diagnostic assessment of acute kidney injury in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2014;60:455–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

