Determining the Location of the Fovea Centralis Via En-Face SLO and Cross-Sectional OCT Imaging in Patients Without Retinal Pathology
- PMID: 34003910
- PMCID: PMC7900853
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.10.2.25
Determining the Location of the Fovea Centralis Via En-Face SLO and Cross-Sectional OCT Imaging in Patients Without Retinal Pathology
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose was to establish the position of the fovea centralis to the optic nerve via en-face, near-infrared spectral domain optical coherence tomography (NIR-OCT) in healthy patients. This may shed light on physiological variability and be used for studying subtle cases of foveal ectopia in macular pathology and after retinal detachment.
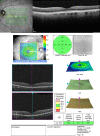
Methods: SD-OCT data of 890 healthy eyes were retrospectively analyzed. Exclusion criteria included axial myopia causing tilting of the optic disc, peripapillary atrophy >1/3 the width of the disc, macular images excluding greater than half of the optic disc, and patients unable to maintain vertical head positioning. Two independent reviewers measured the horizontal and vertical distance from the fovea to the optic disc center and optic disc diameter via cross-sectional and en-face scanning laser ophthalmoloscopy OCT imaging.
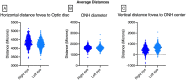
Results: 890 eyes were included in the study. The right and left eyes differed in the horizontal distance from the fovea to the disc center (4359 vs. 4248 µm, P < 0.001) and vertical distance from the fovea to the disc center (464 µm vs. 647, P < 0.001). This corresponded to a smaller angle between the right and left eyes (6.07° vs. 8.67°, P < 0.001). Older age was associated with a larger horizontal (P = 0.008) and vertical distance (0.025). These differences persisted after correcting for axial length in the 487 patients with axial-length data.
Conclusions: This study compares the position of the fovea centralis among individuals without macular pathology on a micron level basis. The significant variability between right and left eyes indicates that contralateral eye evaluation cannot be reliably used. Rather, true foveal ectopia requires assessments of preoperative and postoperative NIR-OCT scans. This finding is relevant to retinal detachment cases and evaluation of subtle foveal ectopia.
Translational relevance: This finding is relevant to retinal detachment cases and evaluation of subtle foveal ectopia.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures



Similar articles
-
The foveal position relative to the optic disc and the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness profile in myopia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Mar 10;55(3):1419-26. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13604. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24508789
-
Parapapillary Gamma Zone and Axial Elongation-Associated Optic Disc Rotation: The Beijing Eye Study.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Feb;57(2):396-402. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18263. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 26842757
-
Optic Disc-Fovea Distance, Axial Length and Parapapillary Zones. The Beijing Eye Study 2011.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 21;10(9):e0138701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138701. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26390438 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of optic disc-fovea distance on the normative classifications of macular inner retinal layers as assessed with OCT in healthy subjects.Br J Ophthalmol. 2019 Jun;103(6):821-825. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-312162. Epub 2018 Aug 12. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30100556 Free PMC article.
-
[Disc-fovea angle adjustment for peripallary retinal nerve fiber layer analysis by a spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Preliminary study].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2016 Feb;39(2):149-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2015.06.011. Epub 2016 Feb 5. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2016. PMID: 26856242 French.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of post-operative foveal location and microstructural changes after pars plana vitrectomy for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment using enhanced-depth imaging optical coherence tomography.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2024 Nov 21;10(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s40942-024-00609-6. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2024. PMID: 39574210 Free PMC article.
-
A New Vessel-Based Method to Estimate Automatically the Position of the Nonfunctional Fovea on Altered Retinography From Maculopathies.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Jul 3;12(7):9. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.7.9. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37418249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brazitikos PD, Androudi S, Christen WG, Stangos NT.. Primary pars plana vitrectomy versus scleral buckle surgery for the treatment of pseudophakic retinal detachment: a randomized clinical trial. Retina. 2005; 25: 957–964. - PubMed
-
- Murtagh PJ, Stephenson KA, Rhatigan M, McElnea EM, Connell PP, Keegan DJ.. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachments: primary reattachment rates and visual outcomes over a 4-year period. Ir J Med Sci. 2019; 189: 355–363. - PubMed
-
- Bilgin AB, Dogan ME, Aysun B, Apaydin KC.. Pars plana vitrectomy with or without intraoperative 360 degrees peripheral endolaser for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment treatment. Int Ophthalmol. 2019; 39: 1687–1694. - PubMed
-
- Ugarte M, Williamson TH.. Horizontal and vertical micropsia following macula-off rhegmatogenous retinal-detachment surgical repair. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244: 1545–1548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

