A Deep Learning Model for Screening Multiple Abnormal Findings in Ophthalmic Ultrasonography (With Video)
- PMID: 34004002
- PMCID: PMC8083108
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.10.4.22
A Deep Learning Model for Screening Multiple Abnormal Findings in Ophthalmic Ultrasonography (With Video)
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to construct a deep learning system for rapidly and accurately screening retinal detachment (RD), vitreous detachment (VD), and vitreous hemorrhage (VH) in ophthalmic ultrasound in real time.
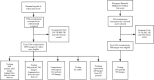
Methods: We used a deep convolutional neural network to develop a deep learning system to screen multiple abnormal findings in ophthalmic ultrasonography with 3580 images for classification and 941 images for segmentation. Sixty-two videos were used as the test dataset in real time. External data containing 598 images were also used for validation. Another 155 images were collected to compare the performance of the model to experts. In addition, a study was conducted to assess the effect of the model in improving lesions recognition of the trainees.
Results: The model achieved 0.94, 0.90, 0.92, 0.94, and 0.91 accuracy in recognizing normal, VD, VH, RD, and other lesions. Compared with the ophthalmologists, the modal achieved a 0.73 accuracy in classifying RD, VD, and VH, which has a better performance than most experts (P < 0.05). In the videos, the model had a 0.81 accuracy. With the model assistant, the accuracy of the trainees improved from 0.84 to 0.94.
Conclusions: The model could serve as a screening tool to rapidly identify patients with RD, VD, and VH. In addition, it also has potential to be a good tool to assist training.
Translational relevance: We developed a deep learning model to make the ultrasound work more accurately and efficiently.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


References
-
- Khairallah M, Kahloun R, Bourne R, et al.. Number of people blind or visually impaired by cataract worldwide and in world regions, 1990 to 2010. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015; 56: 6762–6769. - PubMed
-
- Bello T, Adeoti C.. Ultrasonic assessment in pre-operative cataract patients. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2006; 13: 326–328. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed J, Shaikh FF, Rizwan A, Memon MF.. Evaluation of vitreo-retinal pathologies using B-scan ultrasound. Pak J Ophthalmol. 2009; 25;1–5.
-
- Mitry D, Charteris DG, Fleck BW, Campbell H, Singh J.. The epidemiology of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: geographical variation and clinical associations. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010; 94: 678–684. - PubMed
-
- Pastor J, Fernandez I, De La, Rua ER, et al.. Surgical outcomes for primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachments in phakic and pseudophakic patients: the Retina 1 Project—report 2. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 92: 378–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

