Role of leukotriene pathway and montelukast in pulmonary and extrapulmonary manifestations of Covid-19: The enigmatic entity
- PMID: 34004207
- PMCID: PMC8123523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174196
Role of leukotriene pathway and montelukast in pulmonary and extrapulmonary manifestations of Covid-19: The enigmatic entity
Abstract
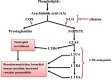
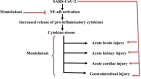
Severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the responsible agent for the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), has its entry point through interaction with angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors, highly expressed in lung type II alveolar cells and other tissues, like heart, pancreas, brain, and vascular endothelium. This review aimed to elucidate the potential role of leukotrienes (LTs) in the pathogenesis and clinical presentation of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and to reveal the critical role of LT pathway receptor antagonists and inhibitors in Covid-19 management. A literature search was done in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar databases to find the potential role of montelukast and other LT inhibitors in the management of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary manifestations triggered by SARS-CoV-2. Data obtained so far underline that pulmonary and extra-pulmonary manifestations in Covid-19 are attributed to a direct effect of SARS-CoV-2 in expressed ACE2 receptors or indirectly through NF-κB dependent induction of a cytokine storm. Montelukast can ameliorate extra-pulmonary manifestations in Covid-19 either directly through blocking of Cys-LTRs in different organs or indirectly through inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: Extrapulmonary manifestations; Leukotriene; Montelukast; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Kuraishy H.M., Al-Naimi M.S., Lungnier C.M., Al-Gareeb A.I. Macrolides and COVID-19: an optimum premise. Biomedical and Biotechnology Research Journal (BBRJ) 2020;4(3):189–197. 1.
-
- Al-Kuraishy H.M., Hussien N.R., Al-Naimi M.S., Al-Buhadily A.K., Al-Gareeb A.I., Lungnier C. Renin–Angiotensin system and fibrinolytic pathway in COVID-19: one-way skepticism. Biomedical and Biotechnology Research Journal (BBRJ) 2020;4(5):33–39.
-
- Al-Kuraishy H.M., Al-Niemi M.S., Hussain N.R., Al-Gareeb A.I., Al-Harchan N.A., Al-Kurashi A.H. In: Kibel A., editor. vol. 2. IntechOpen; London: 2020. The potential role of renin angiotensin system (RAS) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) in COVID-19: navigating the uncharted; pp. 151–165. (Selected Chapters from the Reninangiotensin System).
-
- Al-kuraishy H.M., Al-Maiahy T.J., Al-Gareeb A.I., Musa R.A., Ali Z.H. COVID-19 pneumonia in an Iraqi pregnant woman with preterm delivery. Asian Pacific Journal of Reproduction. 2020;9(3):156.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

