COVID-19: breaking down a global health crisis
- PMID: 34006330
- PMCID: PMC8129964
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-021-00438-7
COVID-19: breaking down a global health crisis
Abstract
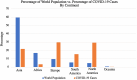
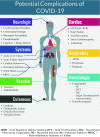
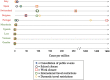
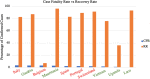
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is the second pandemic of the twenty-first century, with over one-hundred million infections and over two million deaths to date. It is a novel strain from the Coronaviridae family, named Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2); the 7th known member of the coronavirus family to cause disease in humans, notably following the Middle East Respiratory syndrome (MERS), and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (SARS). The most characteristic feature of this single-stranded RNA molecule includes the spike glycoprotein on its surface. Most patients with COVID-19, of which the elderly and immunocompromised are most at risk, complain of flu-like symptoms, including dry cough and headache. The most common complications include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, and cardiovascular manifestations. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is mainly via respiratory droplets, either directly from the air when an infected patient coughs or sneezes, or in the form of fomites on surfaces. Maintaining hand-hygiene, social distancing, and personal protective equipment (i.e., masks) remain the most effective precautions. Patient management includes supportive care and anticoagulative measures, with a focus on maintaining respiratory function. Therapy with dexamethasone, remdesivir, and tocilizumab appear to be most promising to date, with hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferons falling out of favour. Additionally, accelerated vaccination efforts have taken place internationally, with several promising vaccinations being mass deployed. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, countries and stakeholders have taken varying precautions to combat and contain the spread of the virus and dampen its collateral economic damage. This review paper aims to synthesize the impact of the virus on a global, micro to macro scale.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Global & Public Health; Infectious Diseases; Pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organisation . WHO announces COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- Worldometers. Coronavirus Cases - Statistics and Charts. 2020. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/#case-growth....
-
- World Health Organisation. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2020. https://covid19.who.int/.
-
- World Health Organisation. Novel coronavirus-China. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

