Mycobacterium tuberculosis precursor rRNA as a measure of treatment-shortening activity of drugs and regimens
- PMID: 34006838
- PMCID: PMC8131613
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22833-6
Mycobacterium tuberculosis precursor rRNA as a measure of treatment-shortening activity of drugs and regimens
Abstract
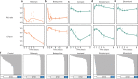
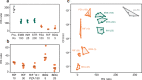
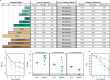
There is urgent need for new drug regimens that more rapidly cure tuberculosis (TB). Existing TB drugs and regimens vary in treatment-shortening activity, but the molecular basis of these differences is unclear, and no existing assay directly quantifies the ability of a drug or regimen to shorten treatment. Here, we show that drugs historically classified as sterilizing and non-sterilizing have distinct impacts on a fundamental aspect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis physiology: ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis. In culture, in mice, and in human studies, measurement of precursor rRNA reveals that sterilizing drugs and highly effective drug regimens profoundly suppress M. tuberculosis rRNA synthesis, whereas non-sterilizing drugs and weaker regimens do not. The rRNA synthesis ratio provides a readout of drug effect that is orthogonal to traditional measures of bacterial burden. We propose that this metric of drug activity may accelerate the development of shorter TB regimens.
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Colorado has filed a patent application entitled “Methods of Evaluating Treatment Efficacy and/or Treatment Duration In Mycobacterial Diseases [Application 16/632,310, filed January 17, 2020, currently pending] pertaining to use of pre-rRNA ratios for monitoring treatment efficacy. Inventors are N.D.W., M.I.V., G.T.R., A.J.L., G.D., G.S., P.N., and J.L.D. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
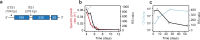

References
-
- World Health Organization. An International Roadmap for Tuberculosis Research (2011).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- K24 AI145806/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL140804/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI135652/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI101714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL087713/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI127300/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090335/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004527/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL143998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI135124/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 206379/Z/17/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- D43 TW009607/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI116295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- IK2 CX000914/CX/CSRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

