Machine learning based differentiation of glioblastoma from brain metastasis using MRI derived radiomics
- PMID: 34006893
- PMCID: PMC8131619
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90032-w
Machine learning based differentiation of glioblastoma from brain metastasis using MRI derived radiomics
Abstract
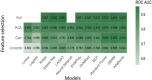
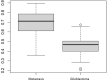
Few studies have addressed radiomics based differentiation of Glioblastoma (GBM) and intracranial metastatic disease (IMD). However, the effect of different tumor masks, comparison of single versus multiparametric MRI (mp-MRI) or select combination of sequences remains undefined. We cross-compared multiple radiomics based machine learning (ML) models using mp-MRI to determine optimized configurations. Our retrospective study included 60 GBM and 60 IMD patients. Forty-five combinations of ML models and feature reduction strategies were assessed for features extracted from whole tumor and edema masks using mp-MRI [T1W, T2W, T1-contrast enhanced (T1-CE), ADC, FLAIR], individual MRI sequences and combined T1-CE and FLAIR sequences. Model performance was assessed using receiver operating characteristic curve. For mp-MRI, the best model was LASSO model fit using full feature set (AUC 0.953). FLAIR was the best individual sequence (LASSO-full feature set, AUC 0.951). For combined T1-CE/FLAIR sequence, adaBoost-full feature set was the best performer (AUC 0.951). No significant difference was seen between top models across all scenarios, including models using FLAIR only, mp-MRI and combined T1-CE/FLAIR sequence. Top features were extracted from both the whole tumor and edema masks. Shape sphericity is an important discriminating feature.
Conflict of interest statement
Other conflict of interest: Girish Bathla has a research grant from Siemens AG, Forchheim, Germany as well as American Cancer Society that is unrelated to the submitted work. Rest of the authors report no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
AI-based classification of three common malignant tumors in neuro-oncology: A multi-institutional comparison of machine learning and deep learning methods.J Neuroradiol. 2024 May;51(3):258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2023.08.007. Epub 2023 Aug 29. J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 37652263
-
Radiomics-based differentiation between glioblastoma and primary central nervous system lymphoma: a comparison of diagnostic performance across different MRI sequences and machine learning techniques.Eur Radiol. 2021 Nov;31(11):8703-8713. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07845-6. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33890149
-
Glioblastoma and Solitary Brain Metastasis: Differentiation by Integrating Demographic-MRI and Deep-Learning Radiomics Signatures.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Sep;60(3):909-920. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29123. Epub 2023 Nov 13. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37955154
-
Radiomic Based Machine Learning Performance for a Three Class Problem in Neuro-Oncology: Time to Test the Waters?Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 24;13(11):2568. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112568. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073840 Free PMC article.
-
An integrative non-invasive malignant brain tumors classification and Ki-67 labeling index prediction pipeline with radiomics approach.Eur J Radiol. 2023 Jan;158:110639. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110639. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Eur J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36463703
Cited by
-
Hemodynamic Imaging in Cerebral Diffuse Glioma-Part B: Molecular Correlates, Treatment Effect Monitoring, Prognosis, and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 5;14(5):1342. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051342. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differentiating Glioblastoma Multiforme from Brain Metastases Using Multidimensional Radiomics Features Derived from MRI and Multiple Machine Learning Models.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 28;2022:2016006. doi: 10.1155/2022/2016006. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36212721 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Intracerebral Tumor Entities with Quantitative Contrast Attenuation and Iodine Mapping in Dual-Layer Computed Tomography.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Oct 15;12(10):2494. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102494. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292183 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance-based imaging biopsy with signatures including topological Betti number features for prediction of primary brain metastatic sites.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023 Dec;46(4):1411-1426. doi: 10.1007/s13246-023-01308-6. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 37603131
-
Artificial intelligence in the radiomic analysis of glioblastomas: A review, taxonomy, and perspective.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 2;12:924245. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.924245. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35982952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artzi, M., Bressler, I. & Ben Bashat, D. Differentiation between glioblastoma, brain metastasis and subtypes using radiomics analysis. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI50, 519–528, doi:10.1002/jmri.26643 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

