Inhibitory influence of cationic Gemini surfactant on the dissolution rate of N80 carbon steel in 15% HCl solution
- PMID: 34006942
- PMCID: PMC8131745
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90031-x
Inhibitory influence of cationic Gemini surfactant on the dissolution rate of N80 carbon steel in 15% HCl solution
Abstract
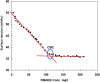
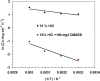
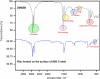
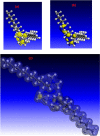
Strong acids are commonly used in petroleum wells to remove scale layers from the surface of N80 C-steel pipe. The corrosive effects of these acids, on the other hand, pose a significant risk to C-steel pipes. For the first time, we discovered the anti-corrosion properties of cationic Gemini surfactant, 1,2-bis(dodecyldimethylammonio) ethane dibromide (DMAEB), for N80 C-steel pipe in acid washing solution (15.0% HCl). The DMAEB, in particular, can reduce the corrosion rate of N80 C-steel by approximately 97%. DMAEB molecules work as a mixed-type corrosion inhibitor, according to electrochemical results. The DMAEB demonstrated a high inhibition effect at high temperatures, as well as high activation energy against the corrosion process. DMAEB's significant performance is primarily due to physical adsorption on the N80 C-steel surface, as confirmed by adsorption isotherms, SEM, EDX, FT-IR, and theoretical studies. Our findings shed new light on the use of Gemini surfactants as corrosion inhibitors in petroleum wells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Jiawei K, Yan J, Kunpeng Z, Pengju R. Experimental investigation on the characteristics of acid-etched fractures in acid fracturing by an improved true tri-axial equipment. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020;184:106471. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106471. - DOI
-
- Yadav M, Sarkar TK, Purkait T. Amino acid compounds as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for N80 steel in HCl solution: Electrochemical and theoretical approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2015;212:731–738. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2015.10.021. - DOI
-
- Brylee DB, Rigoberto CA. Polymeric corrosion inhibitors for the oil and gas industry: Design principles and mechanism. React. Funct. Polym. 2015;95:25–45. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2015.08.006. - DOI
-
- Zheng X, Zhang S, Li W, Gong M, Yin L. Experimental and theoretical studies of two imidazolium-based ionic liquids as inhibitors for mild steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2015;95:168–179. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.03.012. - DOI
-
- Zhang QH, Hou BS, Li YY, Zhu GY, Liu HF, Zhang GA. Two novel chitosan derivatives as high efficient eco-friendly inhibitors for the corrosion of mild steel in acidic solution. Corros. Sci. 2020;164:108346. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108346. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

