Super-resolution imaging of platelet-activation process and its quantitative analysis
- PMID: 34006947
- PMCID: PMC8131365
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89799-9
Super-resolution imaging of platelet-activation process and its quantitative analysis
Abstract
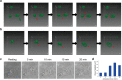
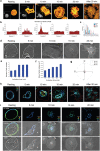
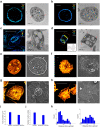
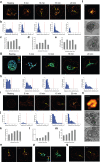
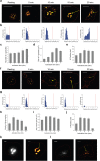
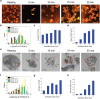
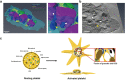
Understanding the platelet activation molecular pathways by characterizing specific protein clusters within platelets is essential to identify the platelet activation state and improve the existing therapies for hemostatic disorders. Here, we employed various state-of-the-art super-resolution imaging and quantification methods to characterize the platelet spatiotemporal ultrastructural change during the activation process due to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) stimuli by observing the cytoskeletal elements and various organelles at nanoscale, which cannot be done using conventional microscopy. Platelets could be spread out with the guidance of actin and microtubules, and most organelles were centralized probably due to the limited space of the peripheral thin regions or the close association with the open canalicular system (OCS). Among the centralized organelles, we provided evidence that granules are fused with the OCS to release their cargo through enlarged OCS. These findings highlight the concerted ultrastructural reorganization and relative arrangements of various organelles upon activation and call for a reassessment of previously unresolved complex and multi-factorial activation processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytoskeletal changes in platelets induced by thrombin and phorbol myristate acetate (PMA).Cell Biol Int. 1998;22(6):429-35. doi: 10.1006/cbir.1998.0271. Cell Biol Int. 1998. PMID: 10328851
-
Cytochemical electron microscopic studies of the action of phorbol myristate acetate on platelets.Am J Pathol. 1974 Mar;74(3):453-66. Am J Pathol. 1974. PMID: 4814897 Free PMC article.
-
Retention of the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex in the isolated platelet cytoskeleton. Effects of separable assembly of platelet pseudopodal and contractile cytoskeletons.J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):1080-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI111475. J Clin Invest. 1984. PMID: 6088580 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets: production, morphology and ultrastructure.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2012;(210):3-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-29423-5_1. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22918725 Review.
-
The molecular basis of platelet biogenesis, activation, aggregation and implications in neurological disorders.Int J Neurosci. 2020 Dec;130(12):1237-1249. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1732372. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Int J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32069430 Review.
Cited by
-
Approaching Thrombospondin-1 as a Potential Target for Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Support Liver Regeneration after Partial Hepatectomy in Mouse and Humans.Cells. 2024 Mar 17;13(6):529. doi: 10.3390/cells13060529. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534373 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in Correlative Super-Resolution Fluorescence Microscopy and Electron Microscopy.Mol Cells. 2022 Jan 31;45(1):41-50. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.5011. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 35114646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The fate of mitochondria during platelet activation.Blood Adv. 2023 Oct 24;7(20):6290-6302. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010423. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 37624769 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Platelet Research Through Live-Cell Imaging: Challenges, Techniques, and Insights.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 16;25(2):491. doi: 10.3390/s25020491. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent development of computational cluster analysis methods for single-molecule localization microscopy images.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Jan 9;21:879-888. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.01.006. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36698968 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

