A Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Text Message Reminders on Asthma Medication Adherence
- PMID: 34007710
- PMCID: PMC6302753
- DOI: 10.24926/iip.v9i3.1370
A Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Text Message Reminders on Asthma Medication Adherence
Abstract
Objective: Cell phone text messaging reminders offers the promise of an efficient technology for the management of chronic diseases, such as asthma. This review aims to evaluate the effectiveness of text message reminders in improving medication adherence for asthma compared to usual care.
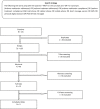
Methods: Randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of text message reminders on adherence to asthma medication were identified from PubMed, Medline, Web of Knowledge EBSCOhost, OvidSP, PsycINFO, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and Cochran Health Technology Assessment databases. Literature searches were restricted to the English language, and no restrictions were imposed on the year and country of publication.
Results: Five studies that were deemed relevant to the systematic review were identified from the literature search. Findings on whether text message reminders improve medication adherence were mixed. However, the review indicates that text-messaging interventions were effective as a means of addressing forgetfulness by reminding patients to take their medications.
Conclusion: This review adds to the body of literature reviewing the effectiveness of emerging technologies in the management of diseases. Despite the fact there is limited evidence across the population of studies to support the effectiveness of text message reminders, such technology represents an important tool to achieve optimal medication adherence among asthmatics.
Keywords: Text messaging; asthma; medication adherence; short message service; systematic review.
© University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing.
References
-
- https://www.cdc.gov/asthma/default.htm. Prevention CfDCa. Asthma. 2018 Jan 10; 2018. (accessed March 16 2018)
-
- Sullivan PW, Ghushchyan V, Navaratnam P, et al. The national cost of asthma among school-aged children in the United States. Annals of allergy, asthma & immunology. 2017;119(3):246–52. e1. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources