Detection of Hepatitis B Virus M204V Mutation Quantitatively via Real-time PCR
- PMID: 34007795
- PMCID: PMC8111100
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00118
Detection of Hepatitis B Virus M204V Mutation Quantitatively via Real-time PCR
Abstract
Background and aims: Drug-resistant DNA mutations of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) affect treatment response in chronic hepatitis B patients. We have established a new, sensitive, specific, accurate and convenient real-time PCR method to detect HBV mutations quantitatively.
Methods: Blood samples were collected from patients showing viral breakthrough, primary nonresponse, or poor response during treatment, and mutations were detected via direct sequencing to assess our method. A plasmid containing the M204V mutation was synthesized and standard curves plotted.
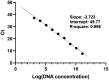
Results: The determination coefficient for linear correlation between Ct and log plasmid copy numbers was 0.996, where Ct value was -3.723log (DNA concentration) +48.647. Coefficients of variation indicated good reproducibility. Correctness was within tolerable bias. Limit of detection was 103 copies/mL. Specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 92.86%, 100%, 96.88%, 100% and 94.74%, respectively.
Conclusions: These results show that our method can be used to detect HBV M204V mutations with the advantages of sensitivity, specificity and efficiency, providing a new choice for monitoring drug resistance.
Keywords: DNA sequencing; Drug-resistance mutation; HBV DNA; Real-time PCR.
© 2021 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus mutation pattern rtL180M+A181C+M204V may contribute to entecavir resistance in clinical practice.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8(1):354-365. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1584018. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019. PMID: 30866789 Free PMC article.
-
[A real-time PCR assay for the quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA and concurrent detection of YMDD motif mutations].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2011 Oct;45(4):664-76. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2011. PMID: 22090297 Turkish.
-
Quantitative detection of the M204V hepatitis B virus minor variants by amplification refractory mutation system real-time PCR combined with molecular beacon technology.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Aug;47(8):2544-50. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00045-09. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19553583 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro susceptibility of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus to adefovir and tenofovir.Antivir Ther. 2004 Jun;9(3):353-63. Antivir Ther. 2004. PMID: 15259898
-
Detection of Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Drug Resistance Mutations Based on Multicolor Melting Curve Analysis.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 Nov;54(11):2661-2668. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00439-16. Epub 2016 Aug 17. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27535686 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: a persistent global problem.Braz J Microbiol. 2023 Jun;54(2):679-689. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-00970-y. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Braz J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37059940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction: Current Techniques, Applications, and Role in COVID-19 Diagnosis.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;13(12):2387. doi: 10.3390/genes13122387. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Simple and Rapid Method for Quantitative Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Drug-resistant Mutations.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021 Apr 28;9(2):139-140. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00135. Epub 2021 Apr 16. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34007793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources