Infliximab-Induced Acute Liver Failure in a Patient With Crohn's Disease Requiring Orthotopic Liver Transplantation
- PMID: 34007859
- PMCID: PMC8126550
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000586
Infliximab-Induced Acute Liver Failure in a Patient With Crohn's Disease Requiring Orthotopic Liver Transplantation
Abstract
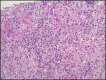
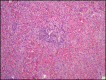
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors are not known to have significant liver toxicity; however, a few case reports state otherwise. We report the case of a 25-year-old man with Crohn's disease who was initiated on infliximab. The patient developed severe mixed hepatocellular and cholestatic liver injury that progressed into acute liver failure. Based on clinical history, laboratory findings, and histology, this was presumed because of the development of autoimmune hepatitis secondary to infliximab. He underwent liver transplantation. The mainstay of treatment in this rare condition involves steroid therapy and possible transplantation. Patients must then avoid anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy for life.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infliximab-induced autoimmune hepatitis requiring liver transplantation.Clin Case Rep. 2019 Sep 27;7(11):2135-2139. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2456. eCollection 2019 Nov. Clin Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31788265 Free PMC article.
-
Generalized Pyoderma Gangrenosum Associated with Ulcerative Colitis: Successful Treatment with Infliximab and Azathioprine.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016 Apr;24(1):83-5. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016. PMID: 27149138
-
Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type B in a Patient with Crohn's Disease Treated with TNF-Alpha Inhibitors Infliximab and Adalimumab.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2019 Sep;27(3):202-204. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2019. PMID: 31542070
-
[Anti-TNF therapy in treatment of luminal Crohn's disease].Acta Med Croatica. 2013 Apr;67(2):179-89. Acta Med Croatica. 2013. PMID: 24471301 Review. Croatian.
-
Acute Liver Failure from Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Antagonists: Report of Four Cases and Literature Review.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Jun;63(6):1654-1666. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5023-6. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29564668 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Therapies and Acute Liver Injury.Toxics. 2024 Jun 8;12(6):421. doi: 10.3390/toxics12060421. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38922101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver Involvement in Celiac Disease and Immune-Mediated Diseases of the Small Bowel.Liver Int. 2025 Aug;45(8):e70206. doi: 10.1111/liv.70206. Liver Int. 2025. PMID: 40679061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scavenging ROS to Alleviate Acute Liver Injury by ZnO-NiO@COOH.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Apr;9(11):e2103982. doi: 10.1002/advs.202103982. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35138033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Highlights of prescribing information. n.d. (https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/103772s5359lbl...). Accessed March 30, 2020.
-
- Kok B, Lester ELW, Lee WM, et al. ; for the United States Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Acute liver failure from tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists: Report of four cases and literature review. Dig Dis Sci 2018;63(6):1654–66. - PubMed
-
- Björnsson ES, Gunnarsson BI, Gröndal G, et al. . Risk of drug-induced liver injury from tumor necrosis factor Antagonists. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13(3):602–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources