Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways Connecting Classical and Rare OI Types
- PMID: 34007986
- PMCID: PMC8755987
- DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnab017
Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways Connecting Classical and Rare OI Types
Abstract
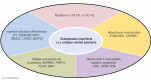
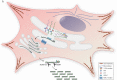
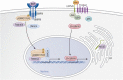
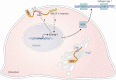
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a phenotypically and genetically heterogeneous skeletal dysplasia characterized by bone fragility, growth deficiency, and skeletal deformity. Previously known to be caused by defects in type I collagen, the major protein of extracellular matrix, it is now also understood to be a collagen-related disorder caused by defects in collagen folding, posttranslational modification and processing, bone mineralization, and osteoblast differentiation, with inheritance of OI types spanning autosomal dominant and recessive as well as X-linked recessive. This review provides the latest updates on OI, encompassing both classical OI and rare forms, their mechanism, and the signaling pathways involved in their pathophysiology. There is a special emphasis on mutations in type I procollagen C-propeptide structure and processing, the later causing OI with strikingly high bone mass. Types V and VI OI, while notably different, are shown to be interrelated by the interferon-induced transmembrane protein 5 p.S40L mutation that reveals the connection between the bone-restricted interferon-induced transmembrane protein-like protein and pigment epithelium-derived factor pathways. The function of regulated intramembrane proteolysis has been extended beyond cholesterol metabolism to bone formation by defects in regulated membrane proteolysis components site-2 protease and old astrocyte specifically induced-substance. Several recently proposed candidate genes for new types of OI are also presented. Discoveries of new OI genes add complexity to already-challenging OI management; current and potential approaches are summarized.
Keywords: IFITM5/BRIL; MBTPS2; PEDF; bone mass; bone mineralization; collagen synthesis; osteogenesis imperfecta; regulated intramembrane proteolysis.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society 2021.
Figures

References
-
- Gatti D, Rossini M, Viapiana O, et al. Teriparatide treatment in adult patients with osteogenesis imperfecta type I. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;93(5):448-452. - PubMed
-
- Nicol L, Srikanth P, Henriksen K, et al. Widespread disturbance in extracellular matrix collagen biomarker responses to teriparatide therapy in osteogenesis imperfecta. Bone. 2021;142:115703. - PubMed
-
- Kuivaniemi H, Tromp G, Prockop DJ. Mutations in collagen genes: causes of rare and some common diseases in humans. Faseb J. 1991;5(7):2052-2060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

