The proprotein convertase furin inhibits IL-13-induced inflammation in airway smooth muscle by regulating integrin-associated signaling complexes
- PMID: 34009050
- PMCID: PMC8321855
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00618.2020
The proprotein convertase furin inhibits IL-13-induced inflammation in airway smooth muscle by regulating integrin-associated signaling complexes
Abstract
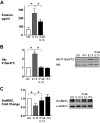
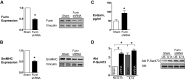
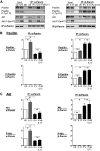
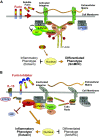
Furin is a proprotein convertase that regulates the activation and the inactivation of multiple proteins including matrix metalloproteinases, integrins, and cytokines. It is a serine endoprotease that localizes to the plasma membrane and can be secreted into the extracellular space. The role of furin in regulating inflammation in isolated canine airway smooth muscle tissues was investigated. The treatment of airway tissues with recombinant furin (rFurin) inhibited the activation of Akt and eotaxin secretion induced by IL-13, and it prevented the IL-13-induced suppression of smooth muscle myosin heavy chain expression. rFurin promoted a differentiated phenotype by activating β1-integrin proteins and stimulating the activation of the adhesome proteins vinculin and paxillin by talin. Activated paxillin induced the binding of Akt to β-parvin IPP [integrin-linked kinase (ILK), PINCH, parvin] complexes, which inhibits Akt activation. Treatment of tissues with a furin inhibitor or the depletion of endogenous furin using shRNA resulted in Akt activation and inflammatory responses similar to those induced by IL-13. Furin inactivation or IL-13 caused talin cleavage and integrin inactivation, resulting in the inactivation of vinculin and paxillin. Paxillin inactivation resulted in the coupling of Akt to α-parvin IPP complexes, which catalyze Akt activation and an inflammatory response. The results demonstrate that furin inhibits inflammation in airway smooth muscle induced by IL-13 and that the anti-inflammatory effects of furin are mediated by activating integrin proteins and integrin-associated signaling complexes that regulate Akt-mediated pathways to the nucleus. Furin may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of inflammatory conditions of the lungs and airways.
Keywords: IL-13; airway inflammation; airway smooth muscle; integrin complexes; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phenotype transitions induced by mechanical stimuli in airway smooth muscle are regulated by differential interactions of parvin isoforms with paxillin and Akt.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):L1036-L1055. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00506.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32130030 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical stimuli and IL-13 interact at integrin adhesion complexes to regulate expression of smooth muscle myosin heavy chain in airway smooth muscle tissue.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):L275-84. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00043.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21642449 Free PMC article.
-
Elastase alters contractility and promotes an inflammatory synthetic phenotype in airway smooth muscle tissues.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Apr 1;314(4):L626-L634. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00334.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29212803 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role for RhoA GTPase in the regulation of airway smooth muscle contraction.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Feb;93(2):129-36. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0388. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25531582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Airway smooth muscle cell as therapeutic target of inflammation.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(1):67-76. doi: 10.2174/092986707779313507. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17266568 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane adhesion junctions regulate airway smooth muscle phenotype and function.Physiol Rev. 2023 Jul 1;103(3):2321-2347. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00020.2022. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36796098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting cytoskeletal biomechanics to modulate airway smooth muscle contraction in asthma.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jan;301(1):108028. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108028. Epub 2024 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39615690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-13 neutralization attenuates carotid artery intimal hyperplasia and increases endothelial cell migration via modulating the JAK-1/STAT-3 signaling pathway.Cell Adh Migr. 2023 Dec;17(1):1-10. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2023.2265158. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Cell Adh Migr. 2023. PMID: 37814455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desai LP, Wu Y, Tepper RS, Gunst SJ. Mechanical stimuli and IL-13 interact at integrin adhesion complexes to regulate expression of smooth muscle myosin heavy chain in airway smooth muscle tissue. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 301: L275–L284, 2011. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00043.2011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hirst SJ, Hallsworth MP, Peng Q, Lee TH. Selective induction of eotaxin release by interleukin-13 or interleukin-4 in human airway smooth muscle cells is synergistic with interleukin-1beta and is mediated by the interleukin-4 receptor alpha-chain. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165: 1161–1171, 2002. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.165.8.2107158. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

