Anti-PD-L1 Therapy Does Not Improve Survival in a Murine Model of Lethal Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia
- PMID: 34009385
- PMCID: PMC8672766
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab274
Anti-PD-L1 Therapy Does Not Improve Survival in a Murine Model of Lethal Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus (SA) bacterial pneumonia is a common cause of sepsis in intensive care units. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) that target programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) have been proposed for the treatment of sepsis. However, in our systematic review of sepsis preclinical models, none of the models examined CPIs in pneumonia.
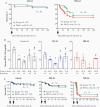
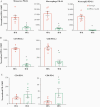
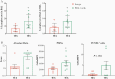
Methods: Mice were inoculated intratracheally with vehicle control, low dose (LD)- or high dose (HD)-SA. Immune cell recruitment and checkpoint molecule expression were examined at 4, 24, and 48 hours after infection. Infected animals, treated with control or anti-PD-L1 antibodies, were assessed for survival, bacterial burden, lung immunophenotypes, and mediator production.
Results: LD-SA and HD-SA produced lethality of 15% and 70%, respectively, by 168 hours. At 24 hours, LD-infected animals exhibited increased lung monocyte PD-L1 expression (P = .0002) but lower bacterial counts (P = .0002) compared with HD animals. By 48 hours, either infection induced lung neutrophil and macrophage PD-L1 expression (P < .0001). Anti-PD-L1 treatment at the time of infection and at 24 hours following infection with low to high doses of SA reduced PD-L1 detection but did not affect survival or bacterial clearance.
Conclusions: Anti-PD-L1 therapy did not alter survival in this pneumonia model. Preclinical studies of additional common pathogens and septic foci are needed.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; immunotherapy; pneumonia; sepsis.
Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2021.
Figures



References
-
- van Vught LA, Klein Klouwenberg PM, Spitoni C, et al. . MARS Consortium . Incidence, risk factors, and attributable mortality of secondary infections in the intensive care unit after admission for sepsis. JAMA 2016; 315:1469–79. - PubMed
-
- Jin HT, Ahmed R, Okazaki T. Role of PD-1 in regulating T-cell immunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2011; 350:17–37. - PubMed
-
- Kinter AL, Godbout EJ, McNally JP, et al. . The common gamma-chain cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 induce the expression of programmed death-1 and its ligands. J Immunol 2008; 181:6738–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

