Hyaluronan, a double-edged sword in kidney diseases
- PMID: 34009465
- PMCID: PMC8960635
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-021-05113-9
Hyaluronan, a double-edged sword in kidney diseases
Abstract
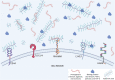
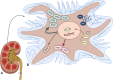
Over the years, hyaluronic acid (HA) has emerged as an important molecule in nephrological and urological studies involving extracellular matrix (ECM) organization, inflammation, tissue regeneration, and viral sensing. During this time, many have noted the perplexing double-edged nature of the molecule, at times promoting pro-fibrotic events and at other times promoting anti-fibrotic events. Different molecular weights of HA can be attributed to these disparities, though most studies have yet to focus on this subtlety. With regard to the kidney, HA is induced in the initial response phase of injury and is subsequently decreased during disease progression of AKI, CKD, and diabetic nephropathy. These and other kidney diseases force patients, particularly pediatric patients, to face dialysis, surgical procedures, and ultimately, transplant. To summarize the current literature for researchers and pediatric nephrologists, this review aims to expound HA and elucidate its paradoxical effects in multiple kidney diseases using studies that emphasize HA molecular weight when available.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury (AKI); Chronic kidney disease (CKD); Diabetic nephropathy; Hyaluronic acid (HA); IgA nephropathy; Kidney cancer; Kidney fibrosis; Obstructive uropathy; Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- (2013) Introduction to Volume One: 2012 USRDS Annual Data Report Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 61(Suppl 1):e1-e22 - PubMed
-
- Inokoshi Y, Tanino Y, Wang X, Sato S, Fukuhara N, Nikaido T, Fukuhara A, Saito J, Frevert CW, Munakata M. Clinical significance of serum hyaluronan in chronic fibrotic interstitial pneumonia. Respirology. 2013;18:1236–1243. - PubMed
-
- Litwiniuk M, Krejner A, Speyrer MS, Gauto AR, Grzela T. Hyaluronic acid in inflammation and tissue regeneration. Wounds. 2016;28:78–88. - PubMed
-
- Wang CT, Lin YT, Chiang BL, Lin YH, Hou SM. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid down-regulates the gene expression of osteoarthritis-associated cytokines and enzymes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with early osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2006;14:1237–1247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

