Feasibility and safety of robotic-assisted total pancreatectomy: a pilot western series
- PMID: 34009627
- PMCID: PMC8184722
- DOI: 10.1007/s13304-021-01079-3
Feasibility and safety of robotic-assisted total pancreatectomy: a pilot western series
Abstract
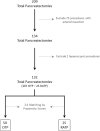
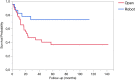
This study was designed to demonstrate non-inferiority of robot-assisted total pancreatectomy (RATP) to open total pancreatectomy (OPT) based on an intention-to-treat analysis, having occurrence of severe post-operative complications (SPC) as primary study endpoint. The two groups were matched (2:1) by propensity scores. Assuming a rate of SPC of 22.5% (non-inferiority margin: 15%; α: 0.05; β: 0.20; power: 80%), a total of 25 patients were required per group. During the study period (October 2008-December 2019), 209 patients received a total pancreatectomy. After application of exclusion and inclusion criteria, matched groups were extracted from an overall cohort of 132 patients (OPT: 107; RATP: 25). Before matching, the two groups were different with respect to prevalence of cardiac disease (24.3% versus 4.0%; p = 0.03), presence of jaundice (45.8% versus 12.0%; p = 0.002), presence of a biliary drainage (23.4% versus 0; p = 0.004), history of weight loss (28.0% versus 8.0%; p = 0.04), and vein involvement (55.1% versus 28.0%) (p = 0.03). After matching, the two groups (OTP: 50; RATP: 25) were well balanced. Regarding primary study endpoint, SPC developed in 13 patients (26.0%) after OTP and in 6 patients (24.0%) after RATP (p = 0.85). Regarding secondary study endpoints, RATP was associated with longer median operating times [475 (408.8-582.5) versus 585 min (525-637.5) p = 0.003]. After a median follow-up time of 23.7 months (10.4-71), overall survival time [22.6 (11.2-81.2) versus NA (27.3-NA) p = 0.006] and cancer-specific survival [22.6 (11.2-NA) versus NA (27.3-NA) p = 0.02] were improved in patients undergoing RATP. In carefully selected patients, robot-assisted total pancreatectomy is non-inferior to open total pancreatectomy regarding occurrence of severe post-operative complications.
Keywords: Pancreatic cancer; Robotic pancreatectomy; Robotic pancreatoduodenectomy; Robotic total pancreatectomy; Surgical complications; Total pancreatectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest. No preregistration exists for the studies reported in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Robotic-Assisted Pancreatic Resections.World J Surg. 2016 Oct;40(10):2497-506. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3565-3. World J Surg. 2016. PMID: 27206401
-
The impact of high body mass index on patients undergoing robotic pancreatectomy: A propensity matched analysis.Surgery. 2020 Mar;167(3):556-559. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Surgery. 2020. PMID: 31837833
-
Comparison between robot-assisted middle pancreatectomy and robot-assisted distal pancreatectomy for benign or low-grade malignant tumours located in the neck of the pancreas: A propensity score matched study.Int J Med Robot. 2021 Jun;17(3):e2219. doi: 10.1002/rcs.2219. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Int J Med Robot. 2021. PMID: 33369060
-
Safety and efficacy for robot-assisted versus open pancreaticoduodenectomy and distal pancreatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Surg Oncol. 2018 Sep;27(3):468-478. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30217304
-
Robotic versus Laparoscopic Distal Pancreatectomy: A Meta-Analysis of Short-Term Outcomes.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 14;11(3):e0151189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151189. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26974961 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Update of CT-Based Radiomics Applications in the Pre-Surgical Prediction of the Risk of Post-Operative Fistula, Resectability Status and Prognosis.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 28;12(23):7380. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237380. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimally invasive versus open total pancreatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2023 Jul 1;109(7):2058-2069. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000392. Int J Surg. 2023. PMID: 37485920 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic left gastric vein reimplantation to prevent gastric venous congestion in total pancreatectomy.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02297-9. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40526213
-
Short-term outcomes and costs analysis of robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy-a retrospective single-center analysis.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023 Aug 8;408(1):299. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-03037-6. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023. PMID: 37552295 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical