Low-power infrared laser modulates telomere length in heart tissue from an experimental model of acute lung injury
- PMID: 34009632
- PMCID: PMC8131880
- DOI: 10.1007/s43630-021-00051-9
Low-power infrared laser modulates telomere length in heart tissue from an experimental model of acute lung injury
Abstract
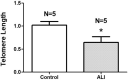
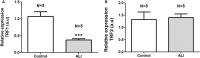
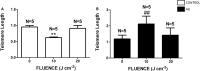
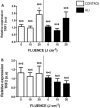
Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome can occur as a result of sepsis. Cardiac dysfunction is a serious component of multi-organ failure caused by severe sepsis. Telomere shortening is related to several heart diseases. Telomeres are associated with the shelterin protein complex, which contributes to the maintenance of telomere length. Low-power infrared lasers modulate mRNA levels of shelterin complex genes. This study aimed to evaluate effects of a low-power infrared laser on mRNA relative levels of genes involved in telomere stabilization and telomere length in heart tissue of an experimental model of acute lung injury caused by sepsis. Animals were divided into six groups, treated with intraperitoneal saline solution, saline solution and exposed to a low-power infrared laser at 10 J cm-2 and 20 J cm-2, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and LPS and, after 4 h, exposed to a low-power infrared laser at 10 J cm-2 and 20 J cm-2. The laser exposure was performed only once. Analysis of mRNA relative levels and telomere length by RT-qPCR was performed. Telomere shortening and reduction in mRNA relative levels of TRF1 mRNA in heart tissues of LPS-induced ALI animals were observed. In addition, laser exposure increased the telomere length at 10 J cm-2 and modulated the TRF1 mRNA relative levels of at 20 J cm-2 in healthy animals. Although the telomeres were shortened and mRNA levels of TRF1 gene were increased in nontreated controls, the low-power infrared laser irradiation increased the telomere length at 10 J cm-2 in cardiac tissue of animals affected by LPS-induced acute lung injury, which suggests that telomere maintenance is a part of the photobiomodulation effect induced by infrared radiation.
Keywords: Low-power laser; Telomerase; Telomere length.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low-power red laser and ultraviolet A LED irradiation reduces mRNA levels from telomere maintenance genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Jun 7;40(1):260. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04520-w. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40481860
-
Low-power infrared laser modulates mRNA levels from genes of base excision repair and genomic stabilization in heart tissue from an experimental model of acute lung injury.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2022 Jul;21(7):1299-1308. doi: 10.1007/s43630-022-00221-3. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35426610
-
Low-power laser alters mRNA levels from DNA repair genes in acute lung injury induced by sepsis in Wistar rats.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Feb;34(1):157-168. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2656-9. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30298300
-
Photobiomodulation prevents DNA fragmentation of alveolar epithelial cells and alters the mRNA levels of caspase 3 and Bcl-2 genes in acute lung injury.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2018 Jul 11;17(7):975-983. doi: 10.1039/c8pp00109j. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29922788
-
Low-power red laser and blue LED modulate telomere maintenance and length in human breast cancer cells.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Oct 7;39(1):248. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04194-w. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39370492
Cited by
-
Low-power red laser and ultraviolet A LED irradiation reduces mRNA levels from telomere maintenance genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Jun 7;40(1):260. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04520-w. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40481860
-
Alleviation of the Genotoxic Effect of Experimental Circulatory Brain Hypoxia in Rat Cornea under the Effect of Infrared Low-Level Laser Radiation.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022 Mar;172(5):549-551. doi: 10.1007/s10517-022-05430-5. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35348956
-
Mechanotransduction, cellular biophotonic activity, and signaling patterns for tissue regeneration.J Biol Chem. 2024 Nov;300(11):107847. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107847. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39357824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causal relationship between telomere length and sepsis: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 5;14(1):5397. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56205-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38443473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- But Y, Kurdowska A, Allen TC. Acute lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine. 2016;140:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Hariri L, Hardin CC. Covid-19, Angiogenesis, and ARDS Endotypes. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;383:182–183. - PubMed
-
- Goh KJ, Choong MC, Cheong EH, Kalimuddin S, Duu Wen S, Phua GC, Chan KS, HajaMohideen S. Rapid progression to acute respiratory distress syndrome: Review of Current Understanding of Critical Illness from COVID-19 Infection. Annals Academy Medicine Singapore. 2020;49:108–118. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

