Energy Decomposition Analysis Reveals the Nature of Lone Pair-π Interactions with Cationic π Systems in Catalytic Acyl Transfer Reactions
- PMID: 34010010
- PMCID: PMC9107076
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c01351
Energy Decomposition Analysis Reveals the Nature of Lone Pair-π Interactions with Cationic π Systems in Catalytic Acyl Transfer Reactions
Abstract
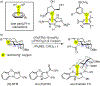
Lone pair-π (LP-π) interactions between Lewis basic heteroatoms, such as oxygen and sulfur, and electron-deficient π systems are important noncovalent interactions. However, they have seldom been used to control catalyst-substrate interactions in catalysis. We performed density functional theory calculations to investigate the strengths of LP-π interactions between different lone pair donors and cationic π systems, and in different complexation geometries. Energy decomposition analysis calculations indicated that the dominant stabilizing force in LP-π complexes is electrostatic interaction and the electrostatic potential surface of the π system predicts the most favorable site for forming LP-π complexes. Benzotetramisole (BTM) is revealed as a privileged acyl transfer catalyst that promotes LP-π interactions because the positive charge of the acylated BTM is delocalized onto the dihydroimidazole ring, which binds strongly with a variety of oxygen and sulfur lone pair donors.
Figures
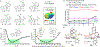
References
-
- Mooibroek TJ; Gamez P; Reedijk J Lone Pair–π Interactions: A New Supramolecular Bond? CrystEngComm 2008, 10 (11), 1501–1515. 10.1039/b812026a. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

