Do Tissues Fixed in a Non-crosslinking Fixative Require a Dedicated Formalin-free Processor?
- PMID: 34010071
- PMCID: PMC8182638
- DOI: 10.1369/00221554211017859
Do Tissues Fixed in a Non-crosslinking Fixative Require a Dedicated Formalin-free Processor?
Abstract
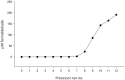
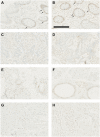
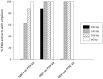
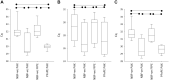
We evaluate the consequences of processing alcohol-fixed tissue in a processor previously used for formalin-fixed tissue. Biospecimens fixed in PAXgene Tissue Fixative were cut into three pieces then processed in a flushed tissue processor previously used for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks (neutral buffered formalin [NBF]+ve), a formalin-free system (NBF-ve), or left unprocessed. Histomorphology and immunohistochemistry were compared using hematoxylin/eosin staining and antibodies for MLH-1, Ki-67, and CK-7. Nucleic acid was extracted using the PAXgene Tissue RNA/DNA kits and an FFPE RNA extraction kit. RNA integrity was assessed using RNA integrity number (RIN), reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (four amplicons), and quantitative RT-PCR (three genes). For DNA, multiplex PCR, quantitative PCR, DNA integrity number, and gel electrophoresis were used. Compared with NBF-ve, RNA from NBF+ve blocks had 88% lower yield and poorer purity; average RIN reduced from 5.0 to 3.8, amplicon length was 408 base pairs shorter, and Cq numbers were 1.9-2.4 higher. Using the FFPE extraction kit rescued yield and purity, but RIN further declined by 1.1 units. Differences between NBF+ve and NBF-ve in respect of DNA, histomorphology, and immunohistochemistry were either non-existent or small in magnitude. Formalin contamination of a tissue processor and its reagents therefore critically reduce RNA yield and integrity. We discuss the available options users can adopt to ameliorate this problem.
Keywords: Illumina; PFPE; ScreenTape; Xylene; degradation; degrade; fixative; formaldehyde; integrity; paraffin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Fox CH, Johnson FB, Whiting J, Roller PP. Formaldehyde fixation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985;33(8):845–53. - PubMed
-
- Blow N. Tissue preparation: tissue issues. Nature. 2007;448(7156):959–64. - PubMed
-
- Robbe P, Popitsch N, Knight SJL, Antoniou P, Becq J, He M, Kanapin A, Samsonova A, Vavoulis DV, Ross MT, Kingsbury Z, Cabes M, Ramos SDC, Page S, Dreau H, Ridout K, Jones LJ, Tuff-Lacey A, Henderson S, Mason J, Buffa FM, Verrill C, Maldonado-Perez D, Roxanis I, Collantes E, Browning L, Dhar S, Damato S, Davies S, Caulfield M, Bentley DR, Taylor JC, Turnbull C, Schuh A. Clinical whole-genome sequencing from routine formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens: pilot study for the 100,000 Genomes Project. Genet Med. 2018;20:1196–205. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaffney EF, Riegman PH, Grizzle WE, Watson PH. Factors that drive the increasing use of FFPE tissue in basic and translational cancer research. Biotech Histochem. 2018;93(5):373–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

