Effect of an inverted seated position with upper arm blood flow restriction on measures of elbow flexors neuromuscular performance
- PMID: 34010275
- PMCID: PMC8133415
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245311
Effect of an inverted seated position with upper arm blood flow restriction on measures of elbow flexors neuromuscular performance
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of the investigation was to determine the concomitant effects of upper arm blood flow restriction (BFR) and inversion on elbow flexors neuromuscular responses.
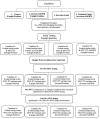
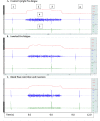
Methods: Randomly allocated, 13 volunteers performed four conditions in a within-subject design: rest (control, 1-min upright position without BFR), control (1-min upright with BFR), 1-min inverted (without BFR), and 1-min inverted with BFR. Evoked and voluntary contractile properties, before, during and after a 30-s maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) exercise intervention were examined as well as pain scale.
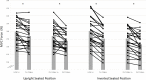
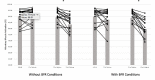
Results: Inversion induced significant pre-exercise intervention decreases in elbow flexors MVC (21.1%, [Formula: see text] = 0.48, p = 0.02) and resting evoked twitch forces (29.4%, [Formula: see text] = 0.34, p = 0.03). The 30-s MVC induced significantly greater pre- to post-test decreases in potentiated twitch force ([Formula: see text] = 0.61, p = 0.0009) during inversion (↓75%) than upright (↓65.3%) conditions. Overall, BFR decreased MVC force 4.8% ([Formula: see text] = 0.37, p = 0.05). For upright position, BFR induced 21.0% reductions in M-wave amplitude ([Formula: see text] = 0.44, p = 0.04). There were no significant differences for electromyographic activity or voluntary activation as measured with the interpolated twitch technique. For all conditions, there was a significant increase in pain scale between the 40-60 s intervals and post-30-s MVC (upright<inversion, and without BFR<BFR).
Conclusion: The concomitant application of inversion with elbow flexors BFR only amplified neuromuscular performance impairments to a small degree. Individuals who execute forceful contractions when inverted or with BFR should be cognizant that force output may be impaired.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuromuscular evaluation of arm-cycling repeated sprints under hypoxia and/or blood flow restriction.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019 Jul;119(7):1533-1545. doi: 10.1007/s00421-019-04143-4. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31011807
-
Effects of an inverted seated position on single and sustained isometric contractions and cardiovascular parameters of trained individuals.Hum Mov Sci. 2015 Apr;40:119-33. doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2014.12.008. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Hum Mov Sci. 2015. PMID: 25553559
-
Neuromuscular fatigue of the elbow flexors during repeated maximal arm cycling sprints: the effects of forearm position.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2021 Jun;46(6):606-616. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2020-0519. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2021. PMID: 33296273
-
Blood flow restriction increases necessary muscle excitation of the elbow flexors during a single high-load contraction.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024 Jun;124(6):1807-1820. doi: 10.1007/s00421-023-05405-y. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38236301
-
The effect of blood flow occlusion during acute low-intensity isometric elbow flexion exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019 Mar;119(3):587-595. doi: 10.1007/s00421-019-04088-8. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30734842 Review.
Cited by
-
The immediate effects of blood flow restriction training on upper limb muscle strength and fatigue level: a meta-analysis.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 1;16:1521145. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1521145. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40666112 Free PMC article.
-
A Study to Identify the Optimum Forearm Floss Band Intensity in 29 Young Adults Performing Blood Flow Restriction Training.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Mar 28;28:e935771. doi: 10.12659/MSM.935771. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35344535 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of blood flow restriction training on post activation potentiation and upper limb muscle activation: a meta-analysis.Front Physiol. 2024 Jul 11;15:1395283. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1395283. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39055689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith DM, McAuliffe J, Johnson MJ, Button DC, Behm DG. Seated inversion adversely affects vigilance tasks and suppresses heart rate and blood pressure. Occup Ergo 2013; 11:153–163. 10.3233/OER-140215 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

