The Mortality and Overall Survival Trends of Primary Liver Cancer in the United States
- PMID: 34010422
- PMCID: PMC8562972
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djab079
The Mortality and Overall Survival Trends of Primary Liver Cancer in the United States
Abstract
Background: Recent trends of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) mortality and outcome remain unknown in the United States. We investigated the recent trends of primary liver cancer (excluding intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma) mortality and HCC stage, treatment, and overall survival (OS) in the United States.
Methods: The National Center for Health Statistics Database was analyzed to investigate the trend of primary liver cancer mortality. We analyzed the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 18 Database to assess the temporal trend of tumor size, stage, treatment, and OS of HCC. We investigated the association between HCC diagnosis year and OS using Cox regression analysis. All statistical tests were 2-sided.
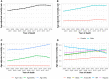
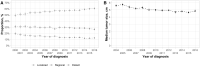
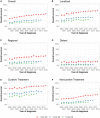
Results: During 2000-2018, liver cancer mortality rates increased until 2013, plateaued during 2013-2016 (annual percent change = 0.1%/y, 95% confidence interval [CI] = -2.1%/y to 2.4%/y, P = .92), and started to decline during 2016-2018 (annual percent change = -1.5%/y, 95% CI = -3.2%/y to 0.2%/y, P = .08). However, mortality continues to increase in American Indian and Alaska Native, individuals aged 65 years or older, and in 33 states. There was a 0.61% (95% CI = 0.53% to 0.69%, P < .001) increase in localized stage HCC and a 0.86-mm (95% CI = -1.10 to -0.62 mm, P < .001) decrease in median tumor size per year. The 1-year OS rate increased from 36.3% (95% CI = 34.3% to 38.3%) to 58.1% (95% CI = 56.9% to 59.4%) during 2000-2015, and the 5-year OS rate almost doubled from 11.7% (95% CI = 10.4% to 13.1%) to 21.3% (95% CI = 20.2% to 22.4%) during 2000-2011. Diagnosis year (per year) (adjusted hazard ratio = 0.96, 95% CI = 0.96 to 0.97) was independently associated with OS in multivariable analysis.
Conclusions: Primary liver cancer mortality rates have started to decline in the United States with demographic and state-level variation. With an increasing detection of localized HCC, the OS of HCC has improved over the past decades.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, et al. ; Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(4):524–548. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

