Thymosin alpha-1 therapy improves postoperative survival after curative resection for solitary hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis
- PMID: 34011034
- PMCID: PMC8137107
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025749
Thymosin alpha-1 therapy improves postoperative survival after curative resection for solitary hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis
Abstract
Thymosin alpha-1 (Tα1) is an immunomodulatory and antiviral agent with potential effects on chronic hepatitis B and liver cancer. Its impact on solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains controversial, so we aimed to investigate the efficacy of Tα1 in solitary HBV-related HCC patients after curative resection.Between May 2010 and April 2016, 468 patients with solitary HBV-related HCC after curative resection were analyzed. Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to minimize confounding variables. Risk factors were identified by the Cox proportional hazards model. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) rates, overall survival (OS) rates, immunological, and virologic response were compared.The median follow up was 60.0 months. Immunological response improved in the Tα1 group compared with the control group (P < .001) but the virologic response was similar between 2 groups after 24 months. Patients with Tα1 therapy had better RFS and OS before (P = .018 and P < .001) and after (P = .006 and P < .001) propensity matching. Multivariate analysis revealed that Tα1 therapy was an independent prognostic factor for both OS (P < .001, HR = 0.308, 95% CI: 0.175-0.541) and RFS (P < .001, HR = 0.381, 95% CI: 0.229-0.633).Tα1 as an adjuvant therapy improves the prognosis of solitary HBV-related HCC patients after curative liver resection.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Figures
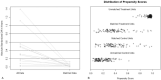


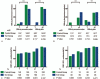
References
-
- Chinese College of Interventionalists CMDA. Chinese Clinical Practice Guidelines for transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2019;27:172–81. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Kuang S, Shan Q, et al. . Can IVIM help predict HCC recurrence after hepatectomy? Eur Radiol 2019;29:5791–803. - PubMed
-
- Yan WT, Quan B, Xing H, et al. . Time to recurrence, but not recurrence-free survival, should be the endpoint used to predict early recurrence after HCC resection. J Hepatol 2019;70:570–1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017ZX10203207-003-0020/State Key Scientific and Technological Research Programs
- 21ZDYF1542/State Key Scientific and Technological Research Programs
- 18HXBH074/Postdoctoral Sustentation Fund of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, China
- 2020HXBH057/Postdoctoral Sustentation Fund of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, China
- 2018SZ0204/Science and Technological Supports Project of Sichuan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

