The metabolite α-KG induces GSDMC-dependent pyroptosis through death receptor 6-activated caspase-8
- PMID: 34012073
- PMCID: PMC8410789
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-021-00506-9
The metabolite α-KG induces GSDMC-dependent pyroptosis through death receptor 6-activated caspase-8
Abstract
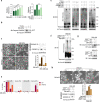
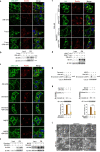
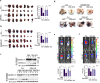
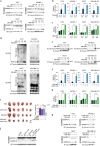
Pyroptosis is a form of regulated cell death mediated by gasdermin family members, among which the function of GSDMC has not been clearly described. Herein, we demonstrate that the metabolite α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) induces pyroptosis through caspase-8-mediated cleavage of GSDMC. Treatment with DM-αKG, a cell-permeable derivative of α-KG, elevates ROS levels, which leads to oxidation of the plasma membrane-localized death receptor DR6. Oxidation of DR6 triggers its endocytosis, and then recruits both pro-caspase-8 and GSDMC to a DR6 receptosome through protein-protein interactions. The DR6 receptosome herein provides a platform for the cleavage of GSDMC by active caspase-8, thereby leading to pyroptosis. Moreover, this α-KG-induced pyroptosis could inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in mouse models. Interestingly, the efficiency of α-KG in inducing pyroptosis relies on an acidic environment in which α-KG is reduced by MDH1 and converted to L-2HG that further boosts ROS levels. Treatment with lactic acid, the end product of glycolysis, builds an improved acidic environment to facilitate more production of L-2HG, which makes the originally pyroptosis-resistant cancer cells more susceptible to α-KG-induced pyroptosis. This study not only illustrates a pyroptotic pathway linked with metabolites but also identifies an unreported principal axis extending from ROS-initiated DR6 endocytosis to caspase-8-mediated cleavage of GSDMC for potential clinical application in tumor therapy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020YFA0803403/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)
- U1905206/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 91853203/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

