The wind-driven formation of cross-shelf sediment plumes in a large lake
- PMID: 34012173
- PMCID: PMC8128696
- DOI: 10.1002/lno.11117
The wind-driven formation of cross-shelf sediment plumes in a large lake
Abstract
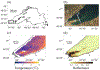
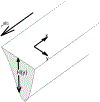
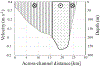
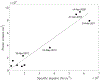
Wind-driven turbidity plumes frequently occur in the western arm of Lake Superior and may represent a significant cross shelf transport mechanism for sediment, nutrient and biota. Here we characterize a plume that formed in late April 2016 using observations from in situ sensors and remote sensing imagery, and estimate the volume of cross shelf transport using both the observations and an idealized analytical model of plume formation. The steady-state, barotropic model is used to determine a relationship between the intensity and duration of a wind event and the volume of water transported from nearshore to offshore during the event. The model transport is the result of nearshore flow in the direction of the wind and a pressure-gradient-driven counter flow in the deeper offshore waters, consistent with observations. The volume of offshore transport associated with the 2016 plume is estimated by both methods to have been on the order of 1010 m3. Analysis of similar events from 2008-2016 shows a strong relationship between specific wind impulse and plume volume. Differences in the intensity and duration of individual events as well as ice cover, which prevents plume formation, lead to interannual variability of offshore transport ranging over an order of magnitude and illustrates how wind-driven processes may contribute to interannual variability of ecosystem functioning.
Keywords: Lake Superior; Physical limnology; coastal processes; cross-shelf transport; plumes; wind-driven processes.
Figures







References
-
- Auer MT, and Bub LA. 2004. Selected Features of the Distribution of Chlorophyll along the Southern Shore of Lake Superior. J. Great Lakes Res. 30 Suppl 1: 269–284, doi:0.1016/S0380-1330(04)70391-3
-
- Austin JA 2013. The potential for Autonomous Underwater Gliders in large lake research. J. Great Lakes Res. 39 Suppl 1: 3–8, doi:10.1016/j.jglr.2013.01.004 - DOI
-
- Beardsley RC, Mofjeld H, Wimbush M, Flagg CN, and Vermersch JA Jr. 1977. Ocean tides and weather-induced bottom pressure fluctuations in the middle-Atlantic bight. J. Geophys. Res. 82: 3175–3182, doi:10.1029/JC082i021p03175. - DOI
-
- Bellinger BJ, and others. 2016. Water quality in the St. Louis River Area of Concern, Lake Superior: Historical and current conditions and delisting implications. J. Great Lakes Res. 42: 28–38, doi:10.1016/j.jglr.2015.11.008 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
