Lipid accumulation and protein modifications of Bruch's membrane in age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 34012894
- PMCID: PMC8077017
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2021.05.19
Lipid accumulation and protein modifications of Bruch's membrane in age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
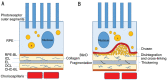
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a progressive retinal disease, which is the leading cause of blindness in western countries. There is an urgency to establish new therapeutic strategies that could prevent or delay the progression of AMD more efficiently. Until now, the pathogenesis of AMD has remained unclear, limiting the development of the novel therapy. Bruch's membrane (BM) goes through remarkable changes in AMD, playing a significant role during the disease course. The main aim of this review is to present the crucial processes that occur at the level of BM, with special consideration of the lipid accumulation and protein modifications. Besides, some therapies targeted at these molecules and the construction of BM in tissue engineering of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells transplantation were listed. Hopefully, this review may provide a reference for researchers engaged in pathogenesis or management on AMD.
Keywords: Bruch's membrane; lipid accumulation; protein modifications; therapy.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

References
-
- Wong WL, Su X, Li X, Cheung CM, Klein R, Cheng CY, Wong TY. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(2):e106–e116. - PubMed
-
- Booij JC, Baas DC, Beisekeeva J, Gorgels TGMF, Bergen AAB. The dynamic nature of Bruch's membrane. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010;29(1):1–18. - PubMed
-
- Zarbin MA. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122(4):598. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
