The proteomic data of liver in mice with hyperlipidemia
- PMID: 34013003
- PMCID: PMC8113717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107050
The proteomic data of liver in mice with hyperlipidemia
Abstract
Fructus Rosae Roxburghii (FRR) has been considered as edible and medicinal fruit possessing antiatherosclerotic effect [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], but the mechanism is still unclear. Hyperlipidemia (HLP) is the material basis for atherosclerosis (AS) formation [6,7]. In this study, total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), lower high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and atherosclerotic index (ASI) in mice were analyzed under the action of FRR juice. Then differentially expressed proteins in liver were further analyzed by using TMT labeling and LC-MS/MS for better understanding the effect and molecular mechanism of FRR on diet-induced hyperlipidemic mice [8]. After the protein extraction and trypsin digestion, TMT labeling proteomic analysis were performed. The functions and KEGG signaling pathways of differentially expressed proteins were analyzed by bioinformatics methods. Hence, the potential antiatherosclerotic mechanism of FRR regulating blood lipids from protein level has great significance to explore new drug targets for AS.
Keywords: Antiatherosclerotic mechanism; Atherosclerosis; Fructus Rosae Roxburghii; Hyperlipidemia; KEGG signaling pathway; TMT proteomic analysis.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have, or could be perceived to have, influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures
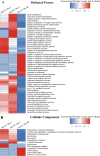


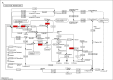




















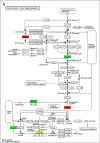










References
-
- Lu X., Bao S. Effect of polysaccharides from Fructus Rosae Roxburghii on stress tolerance and immune function. J. GZ Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2002;19:141–142.
-
- Dai T.T., Yang X.S. Advances in chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Rosa roxburghii. J. GY. Coll. TCM. 2015;37:93–97. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191108.201. - DOI
-
- Zhang C., Liu X., Qiang H. Inhibitory effects of Rosa roxburghii tratt juice on in vitro oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein and on the macrophage growth and cellular cholesteryl ester accumulation induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2001;313:37–43. doi: 10.1016/S0009-8981(01)00647-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xu J., Vidyarthi S.K., Bai W. Nutritional constituents, health benefits and processing of Rosa Roxburghii: a review. J. Func. Foods. 2019;60 doi: 10.1016/J.JFF.2019.103456. - DOI
-
- Burke D.S., Smidt C.R., Vuong L.T. Momordica cochinchinensis, Rosa roxburghii, wolfberry, and sea buckthorn-highly nutritional fruits supported by tradition and science. Curr. Top. Nutraceu. R. 2005;3:59.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

