Association between Birth Region and Time to Tuberculosis Diagnosis among Non-US-Born Persons in the United States
- PMID: 34013876
- PMCID: PMC8153865
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2706.203663
Association between Birth Region and Time to Tuberculosis Diagnosis among Non-US-Born Persons in the United States
Abstract
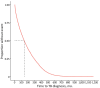
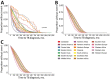
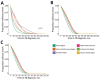
Approximately 90% of tuberculosis (TB) cases among non-US-born persons in the United States are attributable to progression of latent TB infection to TB disease. Using survival analysis, we investigated whether birthplace is associated with time to disease progression among non-US-born persons in whom TB disease developed. We derived a Cox regression model comparing differences in time to TB diagnosis after US entry among 19 birth regions, adjusting for sex, birth year, and age at entry. After adjusting for age at entry and birth year, the median time to TB diagnosis was lowest among persons from Middle Africa, 128 months (95% CI 116-146 months) for male persons and 121 months (95% CI 108-136 months) for female persons. We found time to TB diagnosis among non-US-born persons varied by birth region, which represents a prognostic indicator for progression of latent TB infection to TB disease.
Keywords: Kaplan-Meier estimate; TB; United States; bacteria; emigrants; immigrants; latent tuberculosis; proportional hazards models; respiratory infections; survival analysis; tuberculosis and other mycobacteria.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Reported tuberculosis in the United States, 2018. [cited 2020 Feb 21]. https://www.cdc.gov/tb/statistics/reports/2018/default.htm
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Latent tuberculosis infection: a guide for primary health care providers 2013. [cited 2020 Feb 21]. https://www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/ltbi/pdf/targetedltbi.pdf
-
- Talwar A, Tsang CA, Price SF, Pratt RH, Walker WL, Schmit KM, et al. Tuberculosis—United States, 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:257–62. 10.15585/mmwr.mm6811a2 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

