Increased Incidence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Nontyphoidal Salmonella Infections, United States, 2004-2016
- PMID: 34013877
- PMCID: PMC8153855
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2706.204486
Increased Incidence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Nontyphoidal Salmonella Infections, United States, 2004-2016
Abstract
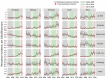
Salmonella is a major cause of foodborne illness in the United States, and antimicrobial-resistant strains pose a serious threat to public health. We used Bayesian hierarchical models of culture-confirmed infections during 2004-2016 from 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention surveillance systems to estimate changes in the national incidence of resistant nontyphoidal Salmonella infections. Extrapolating to the United States population and accounting for unreported infections, we estimated a 40% increase in the annual incidence of infections with clinically important resistance (resistance to ampicillin or ceftriaxone or nonsusceptibility to ciprofloxacin) during 2015-2016 (≈222,000 infections) compared with 2004-2008 (≈159,000 infections). Changes in the incidence of resistance varied by serotype. Serotypes I 4,[5],12:i:- and Enteritidis were responsible for two thirds of the increased incidence of clinically important resistance during 2015-2016. Ciprofloxacin-nonsusceptible infections accounted for more than half of the increase. These estimates can help in setting targets and priorities for prevention.
Keywords: Salmonella; United States; ampicillin; antibiotic resistance; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; ceftriaxone; ciprofloxacin; drug resistance; enteric infections; foodborne diseases; incidence; nontyphoidal; resistance trends.
Figures


Comment in
-
Antimicrobial-Resistant Nontyphoidal Salmonella Infections, United States, 2004-2016.Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Oct;27(10):2746. doi: 10.3201/eid2710.211339. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34546165 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pegues DA, Miller SI. Salmonella Species. In: John E. Bennett, Raphael Dolin, Blaser. MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s principles and practice of infectious diseases. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2020. p. 2725–36.
-
- Krueger AL, Greene SA, Barzilay EJ, Henao O, Vugia D, Hanna S, et al. Clinical outcomes of nalidixic acid, ceftriaxone, and multidrug-resistant nontyphoidal salmonella infections compared with pansusceptible infections in FoodNet sites, 2006-2008. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2014;11:335–41. 10.1089/fpd.2013.1642 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

