The complex role of AIM2 in autoimmune diseases and cancers
- PMID: 34014039
- PMCID: PMC8342223
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.443
The complex role of AIM2 in autoimmune diseases and cancers
Abstract
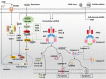
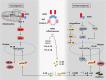
Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) is a novel member of interferon (IFN)-inducible PYHIN proteins. In innate immune cells, AIM2 servers as a cytoplasmic double-stranded DNA sensor, playing a crucial role in the initiation of the innate immune response as a component of the inflammasome. AIM2 expression is increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriasis, and primary Sjogren's syndrome, indicating that AIM2 might be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Meanwhile, AIM2 also plays an antitumorigenesis role in an inflammasome independent-manner. In melanoma, AIM2 is initially identified as a tumor suppressor factor. However, AIM2 is also found to contribute to lung tumorigenesis via the inflammasome-dependent release of interleukin 1β and regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Additionally, AIM2 reciprocally dampening the cGAS-STING pathway causes immunosuppression of macrophages and evasion of antitumor immunity during antibody treatment. To summarize the complicated effect and role of AIM2 in autoimmune diseases and cancers, herein, we provide an overview of the emerging research progress on the function and regulatory pathway of AIM2 in innate and adaptive immune cells, as well as tumor cells, and discuss its pathogenic role in autoimmune diseases, such as SLE, psoriasis, primary Sjogren's syndrome, and cancers, such as melanomas, non-small-cell lung cancer, colon cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, renal carcinoma, and so on, hopefully providing potential therapeutic and diagnostic strategies for clinical use.
Keywords: AIM2; autoimmune diseases; cGAS-STING; cancers.
© 2021 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The DNA sensors AIM2 and IFI16 are SLE autoantigens that bind neutrophil extracellular traps.Elife. 2022 May 24;11:e72103. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72103. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35608258 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2 facilitates the apoptotic DNA-induced systemic lupus erythematosus via arbitrating macrophage functional maturation.J Clin Immunol. 2013 Jul;33(5):925-37. doi: 10.1007/s10875-013-9881-6. Epub 2013 Mar 12. J Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23479181
-
Absent in Melanoma 2 proteins in SLE.Clin Immunol. 2017 Mar;176:42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28062222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon (IFN)-inducible Absent in Melanoma 2 proteins in the negative regulation of the type I IFN response: Implications for lupus nephritis.Cytokine. 2020 Aug;132:154682. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 30904426
-
Review of Excessive Cytosolic DNA and Its Role in AIM2 and cGAS-STING Mediated Psoriasis Development.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Oct 22;17:2345-2357. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S476785. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39464745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Gut-Brain Axis as a Therapeutic Target in Multiple Sclerosis.Cells. 2023 Jul 17;12(14):1872. doi: 10.3390/cells12141872. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pattern-recognition receptors in endometriosis: A narrative review.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1161606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161606. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myricitrin inhibits fibroblast-like synoviocyte-mediated rheumatoid synovial inflammation and joint destruction by targeting AIM2.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 31;13:905376. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.905376. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120327 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cancer by inflammasomes: from inflammation to tumorigenesis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 7;16:1611719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1611719. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40692785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyroptosis of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells as a Potential New Target for Preventing Vascular Diseases.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Jun 1. doi: 10.1007/s10557-024-07578-w. Online ahead of print. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 38822974 Review.
References
-
- DeYoung KL, Ray ME, Su YA, et al. Cloning a novel member of the human interferon‐inducible gene family associated with control of tumorigenicity in a model of human melanoma. Oncogene. 1997;15(4):453‐457. - PubMed
-
- Roberts TL, Idris A, Dunn JA, et al. HIN‐200 proteins regulate caspase activation in response to foreign cytoplasmic DNA. Science. 2009;323(5917):1057‐1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

