Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever in a Large Metropolitan Center, Mexico-United States Border, 2009-2019
- PMID: 34014151
- PMCID: PMC8153879
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2706.191662
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever in a Large Metropolitan Center, Mexico-United States Border, 2009-2019
Abstract
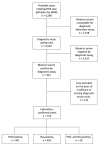
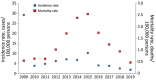
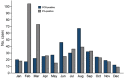
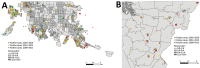
Epidemic levels of Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) have persisted in Mexicali, Mexico, since the initial outbreak was first reported in December 2008. We compared clinical and epidemiologic data of cases in Mexicali during 2009–2019 between patients with an IgG titer reactive with Rickettsia rickettsii bacteria by indirect immunofluorescence antibody (IFA) assay and those who demonstrated DNA of R. rickettsii in a whole blood sample when tested by PCR. We identified 4,290 patients with clinical and epidemiologic features compatible with RMSF; of these, 9.74% tested positive by IFA and 8.41% by PCR. Overall, 140 patients died (11-year case-fatality rate 17.97%). Substantial differences in the frequency of commonly recognized clinical characteristics of RMSF were identified between PCR-positive and IFA-positive cases. The Mexicali epidemic is unique in its size and urban centralization. Cases confirmed by PCR most accurately reflect the clinical profile of RMSF.
Keywords: Mexicali; Mexico; Rhipicephalus sanguineus; Rickettsia rickettsii; Rocky Mountain spotted fever; United States; bacteria; bacterial infections; epidemiology; rickettsial diseases; tickborne diseases; vector-borne infections; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Martínez-Medina MA, Alvarez-Hernández G, Padilla-Zamudioa JG, Rojas-Guerra MG. Fiebre manchada de las Montañas Rocosas en niños: consideraciones clínicas y epidemiológicas. Gac Med Mex. 2007;143:137–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

