Three-Year Follow-up of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy With or Without Anthracyclines in the Presence of Dual ERBB2 Blockade in Patients With ERBB2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Secondary Analysis of the TRAIN-2 Randomized, Phase 3 Trial
- PMID: 34014249
- PMCID: PMC8138752
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1371
Three-Year Follow-up of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy With or Without Anthracyclines in the Presence of Dual ERBB2 Blockade in Patients With ERBB2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Secondary Analysis of the TRAIN-2 Randomized, Phase 3 Trial
Abstract
Importance: Primary analysis of the TRAIN-2 study showed high pathologic complete response rates after neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without anthracyclines plus dual ERBB2 (formerly HER2) blockade.
Objective: To evaluate 3-year event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) of an anthracycline-free and anthracycline-containing regimen with dual ERBB2 blockade in patients with stage II and III ERBB2-positive breast cancer.
Design, setting, and participants: A total of 438 patients with stage II and III ERBB2-positive breast cancer were enrolled in this randomized, clinical, open-label phase 3 trial across 37 hospitals in the Netherlands from December 9, 2013, until January 14, 2016. Follow-up analyses were performed after a median follow-up of 48.8 months (interquartile range, 44.1-55.2 months). Analysis was performed on an intention-to-treat basis.
Interventions: Participants were randomly assigned on a 1:1 basis, stratified by age, tumor stage, nodal stage, and estrogen receptor status, to receive 3 cycles of fluorouracil (500 mg/m2), epirubicin (90 mg/m2), and cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2), followed by 6 cycles of paclitaxel and carboplatin or 9 cycles of paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 days 1 and 8) and carboplatin (area under the concentration-time curve, 6 mg/mL/min). Both groups received trastuzumab (6 mg/kg; loading dose 8 mg/kg) and pertuzumab (420 mg intravenously; loading dose 840 mg) every 3 weeks.
Main outcomes and measures: Three-year EFS, OS, and safety.
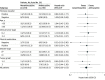
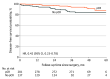
Results: A total of 438 women were randomized, with 219 per group (anthracycline group, median age, 49 years [interquartile range, 43-55 years]; and nonanthracycline group, median age, 48 years [interquartile range, 43-56 years]). A total of 23 EFS events (10.5%) occurred in the anthracycline group and 21 EFS events (9.6%) occurred in the nonanthracycline group (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.50-1.63; favoring nonanthracyclines). Three-year EFS estimates were 92.7% (95% CI, 89.3%-96.2%) in the anthracycline group and 93.6% (95% CI, 90.4%-96.9%) in the nonanthracycline group and 3-year OS estimates were 97.7% (95% CI, 95.7%-99.7%) in the anthracycline group and 98.2% (95% CI, 96.4%-100%) in the nonanthracycline group. The results were irrespective of hormone receptor and nodal status. A decline in left ventricular ejection fraction of 10% or more from baseline to less than 50% was more common in patients who received anthracyclines than those who did not (17 of 220 [7.7%] vs 7 of 218 [3.2%]; P = .04). Two patients treated with anthracyclines developed acute leukemia.
Conclusions and relevance: This follow-up analysis of the TRAIN-2 study shows similar 3-year EFS and OS estimates with or without anthracyclines in patients with stage II and III ERBB2-positive breast cancer. Anthracycline use is associated with increased risk of febrile neutropenia, cardiotoxic effects, and secondary malignant neoplasms.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01996267.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Anthracycline Use in ERBB2-Positive Breast Cancer: It Is Time to Re-TRAIN.JAMA Oncol. 2021 Jul 1;7(7):975-977. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1314. JAMA Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34014297 No abstract available.
References
-
- Slamon D, Eiermann W, Robert N, et al. Abstract S5-04: ten year follow-up of BCIRG-006 comparing doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC→T) with doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel and trastuzumab (AC→TH) with docetaxel, carboplatin and trastuzumab (TCH) in HER2+ early breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2016;76 (suppl 4):S5-04. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.SABCS15-S5-04 - DOI
-
- van Ramshorst MS, van der Voort A, van Werkhoven ED, et al. ; Dutch Breast Cancer Research Group (BOOG) . Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without anthracyclines in the presence of dual HER2 blockade for HER2-positive breast cancer (TRAIN-2): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(12):1630-1640. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30570-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schneeweiss A, Chia S, Hickish T, et al. Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab in combination with standard neoadjuvant anthracycline-containing and anthracycline-free chemotherapy regimens in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: a randomized phase II cardiac safety study (TRYPHAENA). Ann Oncol. 2013;24(9):2278-2284. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt182 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

