The diagnostic accuracy of seven commercial molecular in vitro SARS-CoV-2 detection tests: a rapid meta-analysis
- PMID: 34015984
- PMCID: PMC8171007
- DOI: 10.1080/14737159.2021.1933449
The diagnostic accuracy of seven commercial molecular in vitro SARS-CoV-2 detection tests: a rapid meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the accuracy parameters of seven commercial molecular in vitro diagnostic tests for detecting SARS-CoV-2.
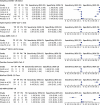
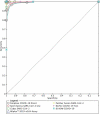
Methods: Studies evaluating the accuracy of seven different commercial molecular diagnostic tests for detecting SARS-CoV-2 (Cepheid Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test, Simplexa COVID-19 Direct, Abbott ID NOW COVID-19, Cobas SARS-CoV-2, Allplex 2019-nCoV Assay, Panther Fusion SARS-CoV-2, and BioFire COVID-19 Test) were included. The quality of the included studies was assessed using the QUADAS-2 checklist. A bivariate random-effects regression model was implemented.
Results: Meta-analysis of 12 included studies showed that the performances of commercial COVID-19 molecular in vitro diagnostic tests were high, with a summary sensitivity of 95.9% (95% CI 93.9-97.2%, I2 = 60.22%) and specificity of 97.2% (95% CI 95.5-98.3%, I2 = 56.66%). Among seven evaluated tests, the Abbott ID NOW COVID-19 and Simplexa COVID-19 Direct displayed lower sensitivity (91.6%, 95% CI 80.5-96.6% and 92%, 95% CI 86.2-95.5, respectively).
Conclusion: All evaluated tests showed good accuracy. However, the slightly lower sensitivity observed in the Abbott ID Now COVID-19 and Simplexa COVID-19 Direct should be considered when deciding on a test platform. Moreover, the diagnostic accuracy of COVID-19 commercial diagnostic tests should be weighed against their ease of use and speed.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; diagnostic accuracy; diagnostic performance; molecular in vitro diagnostic tests.
Figures


References
-
- Ulhaq ZS, Soraya GV.. Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody treatment for severe COVID-19 and the potential implication of IL-6 gene polymorphisms in novel coronavirus pneumonia. Med Clin (Barc) [Internet]. 2020. [cited 2020 August7];155:548–556. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7351402/ - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
