The tumor immune microenvironment and immune-related signature predict the chemotherapy response in patients with osteosarcoma
- PMID: 34016089
- PMCID: PMC8138974
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08328-z
The tumor immune microenvironment and immune-related signature predict the chemotherapy response in patients with osteosarcoma
Abstract
Background: Genome-wide expression profiles have been shown to predict the response to chemotherapy. The purpose of this study was to develop a novel predictive signature for chemotherapy in patients with osteosarcoma.
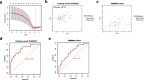
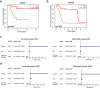
Methods: We analysed the relevance of immune cell infiltration and gene expression profiles of the tumor samples of good responders with those of poor responders from the TARGET and GEO databases. Immune cell infiltration was evaluated using a single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) and the CIBERSORT algorithm between good and poor chemotherapy responders. Differentially expressed genes were identified based on the chemotherapy response. LASSO regression and binary logistic regression analyses were applied to select the differentially expressed immune-related genes (IRGs) and developed a predictive signature in the training cohort. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was employed to assess and validate the predictive accuracy of the predictive signature in the validation cohort.
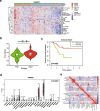
Results: The analysis of immune infiltration showed a positive relationship between high-level immune infiltration and good responders, and T follicular helper cells and CD8 T cells were significantly more abundant in good responders with osteosarcoma. Two hundred eighteen differentially expressed genes were detected between good and poor responders, and a five IRGs panel comprising TNFRSF9, CD70, EGFR, PDGFD and S100A6 was determined to show predictive power for the chemotherapy response. A chemotherapy-associated predictive signature was developed based on these five IRGs. The accuracy of the predictive signature was 0.832 for the training cohort and 0.720 for the validation cohort according to ROC analysis.
Conclusions: The novel predictive signature constructed with five IRGs can be effectively utilized to predict chemotherapy responsiveness and help improve the efficacy of chemotherapy in patients with osteosarcoma.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Immune-related gene; Osteosarcoma; Predictive signature; Tumor immune microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Pullan JE, Budh DP. StatPearls. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2020, StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2020. Primary Bone Cancer.
-
- Eaton BR, Schwarz R, Vatner R, Yeh B, Claude L, Indelicato DJ, et al. Osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020:e28352:S1-7. - PubMed
-
- Zhu W, Zhu L, Bao Y, Zhong X, Chen Y, Wu Q. Clinical evaluation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for osteosarcoma. J BUON. 2019;24(3):1181–1185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

