Conditioned medium from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis
- PMID: 34016178
- PMCID: PMC8139053
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-021-02366-x
Conditioned medium from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis
Abstract
Background: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can improve cutaneous wound healing via the secretion of growth factors. However, the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs varies depending upon their source. Induced pluripotent stem cells are emerging as a promising source of MSCs with the potential to overcome several limitations of adult MSCs. This study compared the effectiveness of conditioned medium of MSCs derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iMSC-CdM) with that derived from umbilical cord MSCs (uMSC-CdM) in a mouse cutaneous wound healing model. We also investigated the mechanisms of protection.
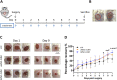
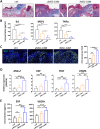
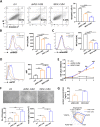
Methods: The iMSC-CdM or uMSC-CdM were topically applied to mice cutaneous wound model. The recovery rate, scar formation, inflammation and angiogenesis were measured. We compared angiogenesis cytokine expression between iMSC-CdM and uMSC-CdM and their protective effects on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) under H2O2-induced injury. The effects of iMSC-CdM on energy metabolism, mitochondria fragmentation and apoptosis were measured.
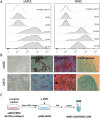
Results: Topical application of iMSC-CdM was superior to the uMSC-CdM in accelerating wound closure and enhancing angiogenesis. Expression levels of angiogenetic cytokines were higher in iMSC-CdM than they were in uMSC-CdM. The iMSC-CdM protected HUVECs from H2O2 induced injury more effectively than uMSC-CdM did. Administration of iMSC-CdM stimulated HUVEC proliferation, tube formation and energy metabolism via the ERK pathway. Mechanistically, iMSC-CdM inhibited H2O2-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and apoptosis of HUVECs.
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings indicate that iMSC-CdM is more effective than uMSC-CdM in treating cutaneous wounds, and in this way, iMSC-CdM may serve as a more constant and sustainable source for cell-free therapeutic approach.
Keywords: Conditioned medium; Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells; Mitochondria dysfunction; Wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platelet-rich plasma improves the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing their secretion of angiogenic factors in a combined radiation and wound injury model.Exp Dermatol. 2020 Feb;29(2):158-167. doi: 10.1111/exd.14042. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Exp Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31560791
-
The Healing Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Radiation-Induced Skin Wounds in Rats.Cell Transplant. 2019 Jan;28(1):105-115. doi: 10.1177/0963689718807410. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30350716 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of exosomes secreted by induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells and synovial membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Mar 9;8(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0510-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28279188 Free PMC article.
-
Using Pre-Clinical Studies to Explore the Potential Clinical Uses of Exosomes Secreted from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem cells.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Oct;20(6):793-809. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00557-6. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37651091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Acquire Rejuvenation and Reduced Heterogeneity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 16;9:717772. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.717772. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34604216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of mesenchymal stromal cells from urine-derived iPSCs of pediatric brain tumor patients.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 26;14:1022676. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1022676. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776860 Free PMC article.
-
HATMSC Secreted Factors in the Hydrogel as a Potential Treatment for Chronic Wounds-In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 12;22(22):12241. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212241. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830121 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Fabrication of Human Corneal Stromal Cell Spheroids and Promoting Cell Stemness Based on 3D-Printed Derived PDMS Microwell Platform.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 19;15(3):438. doi: 10.3390/biom15030438. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149974 Free PMC article.
-
The application potential of iMSCs and iMSC-EVs in diseases.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 29;12:1434465. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1434465. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39135947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of stem cell therapy for atherosclerosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Apr;479(4):779-791. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04762-8. Epub 2023 May 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37178375 Review.
References
-
- Hsieh JY, Wang HW, Chang SJ, Liao KH, Lee IH, Lin WS, Wu CH, Lin WY, Cheng SM. Mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord express preferentially secreted factors related to neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072604. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

