HER2-positive breast cancer and tyrosine kinase inhibitors: the time is now
- PMID: 34016991
- PMCID: PMC8137941
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-021-00265-1
HER2-positive breast cancer and tyrosine kinase inhibitors: the time is now
Abstract
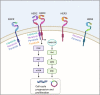
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positive breast cancer accounts for 20-25% of all breast cancers. Multiple HER2-targeted therapies have been developed over the last few years, including the tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) lapatinib, neratinib, tucatinib, and pyrotinib. These drugs target HER2 and other receptors of the epidermal growth factor receptor family, therefore each has unique efficacy and adverse event profile. HER2-directed TKIs have been studied in the early stage and advanced settings and have shown promising responses. There is increasing interest in utilizing these drugs in combination with chemotherapy and /or other HER2-directed agents in patients with central nervous system involvement, TKIs have shown to be effective in this setting for which treatment options have been previously limited and the prognosis remains poor. The aim of this review is to summarize currently approved TKIs for HER2+ breast, key clinical trials, and their use in current clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
I.S has nothing to disclose. S.M.S.: Member, independent data monitoring committee: AstraZeneca. Consulting: Athenex, Daiichi-Sankyo, Silverback Therapeutics, Exact Sciences (Genomic Health), Beijing Medical Foundation, Natera, AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche. Nonpromotional speaking: Genentech/Roche. Research to institution: Genentech/Roche, Kailos Genetics. Third party writing assistance: Genentech/Roche.
Figures


References
-
- Ferlay J. E. M. et al.Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today (WHO, 2018).
-
- Institute, N. C. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program (www.seer.cancer.gov) SEER*Stat Database: Mortality - All COD, Aggregated With State, Total U.S. (1969-2017) (NIH, 2019).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

