QPLOT Neurons-Converging on a Thermoregulatory Preoptic Neuronal Population
- PMID: 34017237
- PMCID: PMC8130930
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.665762
QPLOT Neurons-Converging on a Thermoregulatory Preoptic Neuronal Population
Abstract
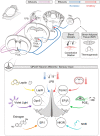
The preoptic area of the hypothalamus is a homeostatic control center. The heterogeneous neurons in this nucleus function to regulate the sleep/wake cycle, reproduction, thirst and hydration, as well as thermogenesis and other metabolic responses. Several recent studies have analyzed preoptic neuronal populations and demonstrated neuronal subtype-specific roles in suppression of thermogenesis. These studies showed similar thermogenesis responses to chemogenetic modulation, and similar synaptic tracing patterns for neurons that were responsive to cold, to inflammatory stimuli, and to violet light. A reanalysis of single-cell/nucleus RNA-sequencing datasets of the preoptic nucleus indicate that these studies have converged on a common neuronal population that when activated, are sufficient to suppress thermogenesis. Expanding on a previous name for these neurons (Q neurons, which reflect their ability to promote quiescence and expression of Qrfp), we propose a new name: QPLOT neurons, to reflect numerous molecular markers of this population and to capture its broader roles in metabolic regulation. Here, we summarize previous findings on this population and present a unified description of QPLOT neurons, the excitatory preoptic neuronal population that integrate a variety of thermal, metabolic, hormonal and environmental stimuli in order to regulate metabolism and thermogenesis.
Keywords: Leptin receptor; Opn5; PTGER3; QRFP; Tacr3; neuropsin; thermoregulation; torpor.
Copyright © 2021 Upton, D’Souza and Lang.
Conflict of interest statement
The Lang lab has a sponsored research agreement with BIOS Lighting Inc. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

