Biological activity evaluations of chemical constituents derived from Mongolian medicinal forage plants and their applications in combating infectious diseases and addressing health problems in humans and livestock
- PMID: 34018093
- PMCID: PMC8137442
- DOI: 10.1007/s11418-021-01529-7
Biological activity evaluations of chemical constituents derived from Mongolian medicinal forage plants and their applications in combating infectious diseases and addressing health problems in humans and livestock
Abstract
Mongolian nomadic people possess traditional knowledge of wild plants that grow in their areas of habitation. Many of these are forage plants in nature and are consumed by livestock. However, these plants are known to have medicinal and/or toxic properties. To establish a scientific understanding of the plants, and in turn, offer sound knowledge on their applications and effective use, it is essential to collect data pertaining to the chemical constituents of each plant. Therefore, the first objective of this study was to identify and determine the structural constituents of the forage plants that were available to our research group. Furthermore, in an attempt to demonstrate the biological activities of the isolated chemical compounds, we focused on solving some of the social issues affecting Mongolian communities, including protozoan diseases affecting livestock, vectors of infectious diseases, and the general health of humans and their livestock. The results of the chemical constituents derived from Mongolian medicinal plants and their biological activities that were studied in the recent decade are also described herein.
Keywords: Chemical; Constituents; Forage; Medicinal; Mongolian; Native.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
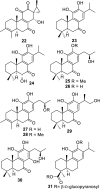
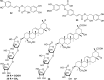
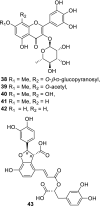
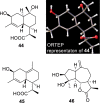
References
-
- Urgamal M, Gundegmaa V, Baasanmunkh Sh, Oyuntsetseg B, Darikhand D, Munkh-Erdene T. Additions to the vascular flora of Mongolia—IV. Proc Mongolian Acad Sci. 2019;59:41–53.
-
- Ministry of food, agriculture and light industry of Mongolia. Sixth national report to the convention on biological diversity. https://www.cbd.int/doc/nr/nr-06/mn-nr-06-en.pdf. Accessed 12th January 2021.
-
- Takano F, Yoshizaki F, Fushiya S, Hayasaka H, Ohba K, Batkhuu J, Sanchir C, Boldsaikhan B. Mongolian traditional medicine and medicinal plants. Kampo Med. 2003;54:963–972. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.54.963. - DOI
-
- Pitschmann A, Purevsuren S, Obmann A, Natsagdorj D, Gunbilig D, Narantuya S, Kletter Ch, Glasl S. Traditional Mongolian Medicine: history and status quo. Phytochem Rev. 2013;12:943–959. doi: 10.1007/s11101-013-9321-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

