Automatically Diagnosing Disk Bulge and Disk Herniation With Lumbar Magnetic Resonance Images by Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks: Method Development Study
- PMID: 34018488
- PMCID: PMC8178733
- DOI: 10.2196/14755
Automatically Diagnosing Disk Bulge and Disk Herniation With Lumbar Magnetic Resonance Images by Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks: Method Development Study
Abstract
Background: Disk herniation and disk bulge are two common disorders of lumbar intervertebral disks (IVDs) that often result in numbness, pain in the lower limbs, and lower back pain. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is one of the most efficient techniques for detecting lumbar diseases and is widely used for making clinical diagnoses at hospitals. However, there is a lack of efficient tools for effectively interpreting massive amounts of MR images to meet the requirements of many radiologists.
Objective: The aim of this study was to present an automatic system for diagnosing disk bulge and herniation that saves time and can effectively and significantly reduce the workload of radiologists.
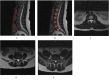
Methods: The diagnosis of lumbar vertebral disorders is highly dependent on medical images. Therefore, we chose the two most common diseases-disk bulge and herniation-as research subjects. This study is mainly about identifying the position of IVDs (lumbar vertebra [L] 1 to L2, L2-L3, L3-L4, L4-L5, and L5 to sacral vertebra [S] 1) by analyzing the geometrical relationship between sagittal and axial images and classifying axial lumbar disk MR images via deep convolutional neural networks.
Results: This system involved 4 steps. In the first step, it automatically located vertebral bodies (including the L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, and S1) in sagittal images by using the faster region-based convolutional neural network, and our fourfold cross-validation showed 100% accuracy. In the second step, it spontaneously identified the corresponding disk in each axial lumbar disk MR image with 100% accuracy. In the third step, the accuracy for automatically locating the intervertebral disk region of interest in axial MR images was 100%. In the fourth step, the 3-class classification (normal disk, disk bulge, and disk herniation) accuracies for the L1-L2, L2-L3, L3-L4, L4-L5, and L5-S1 IVDs were 92.7%, 84.4%, 92.1%, 90.4%, and 84.2%, respectively.
Conclusions: The automatic diagnosis system was successfully built, and it could classify images of normal disks, disk bulge, and disk herniation. This system provided a web-based test for interpreting lumbar disk MR images that could significantly improve diagnostic efficiency and standardized diagnosis reports. This system can also be used to detect other lumbar abnormalities and cervical spondylosis.
Keywords: deep learning; disk bulge; disk herniation; image classification; object localization.
©Qiong Pan, Kai Zhang, Lin He, Zhou Dong, Lei Zhang, Xiaohang Wu, Yi Wu, Yanjun Gao. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (https://medinform.jmir.org), 21.05.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Percent spinal canal compromise on MRI utilized for predicting the need for surgical treatment in single-level lumbar intervertebral disc herniation.Spine J. 2005 Nov-Dec;5(6):608-14. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2005.05.384. Spine J. 2005. PMID: 16291099
-
Familial predisposition for lumbar degenerative disc disease. A case-control study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998 May 1;23(9):1029-34. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199805010-00013. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998. PMID: 9589542
-
Retroperitoneal oblique corridor to the L2-S1 intervertebral discs: an MRI study.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016 Feb;24(2):248-255. doi: 10.3171/2015.3.SPINE13976. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016. PMID: 26451662
-
A Deep Learning Model for Automatic Detection and Classification of Disc Herniation in Magnetic Resonance Images.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022 Dec;26(12):6036-6046. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2022.3209585. Epub 2022 Dec 7. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022. PMID: 36155472 Review.
-
L5 root compression resulting from an L2-L3 disc herniation.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2003 Aug;32(8):392-4. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2003. PMID: 12943341 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learning system for screening AIDS-related cytomegalovirus retinitis with ultra-wide-field fundus images.Heliyon. 2024 May 15;10(10):e30881. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30881. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38803983 Free PMC article.
-
Are current machine learning applications comparable to radiologist classification of degenerate and herniated discs and Modic change? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2023 Nov;32(11):3764-3787. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-07718-0. Epub 2023 May 8. Eur Spine J. 2023. PMID: 37150769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Computer Aided Diagnosis in Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 14;19(10):5971. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19105971. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35627508 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic detection, classification, and segmentation of sagittal MR images for diagnosing prolapsed lumbar intervertebral disc.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):593. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84301-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747557 Free PMC article.
-
Policy Learning for Actively Labeled Sample Selection on Lumbar Semi-supervised Classification.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Feb;38(1):165-176. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01167-x. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 39020159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vos T, Flaxman A, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon J, Abdalla S, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Ackerman I, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Ali MK, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Bahalim AN, Barker-Collo S, Barrero LH, Bartels DH, Basáñez MG, Baxter A, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bernabé E, Bhalla K, Bhandari B, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Black JA, Blencowe H, Blore JD, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Bonaventure A, Boufous S, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Braithwaite T, Brayne C, Bridgett L, Brooker S, Brooks P, Brugha TS, Bryan-Hancock C, Bucello C, Buchbinder R, Buckle G, Budke CM, Burch M, Burney P, Burstein R, Calabria B, Campbell B, Canter CE, Carabin H, Carapetis J, Carmona L, Cella C, Charlson F, Chen H, Cheng ATA, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahiya M, Dahodwala N, Damsere-Derry J, Danaei G, Davis A, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Dellavalle R, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Derrett S, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dherani M, Diaz-Torne C, Dolk H, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Edmond K, Elbaz A, Ali SE, Erskine H, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ewoigbokhan SE, Farzadfar F, Feigin V, Felson DT, Ferrari A, Ferri CP, Fèvre EM, Finucane MM, Flaxman S, Flood L, Foreman K, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FGR, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabbe BJ, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Ganatra HA, Garcia B, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gmel G, Gosselin R, Grainger R, Groeger J, Guillemin F, Gunnell D, Gupta R, Haagsma J, Hagan H, Halasa YA, Hall W, Haring D, Haro JM, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Higashi H, Hill C, Hoen B, Hoffman H, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Huang JJ, Ibeanusi SE, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jarvis D, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Jonas JB, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Kawakami N, Keren A, Khoo JP, King CH, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lalloo R, Laslett LL, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Lee YY, Leigh J, Lim SS, Limb E, Lin JK, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Liu W, Loane M, Ohno SL, Lyons R, Ma J, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Malekzadeh R, Mallinger L, Manivannan S, Marcenes W, March L, Margolis DJ, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGill N, McGrath J, Medina-Mora ME, Meltzer M, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Meyer AC, Miglioli V, Miller M, Miller TR, Mitchell PB, Mocumbi AO, Moffitt TE, Mokdad AA, Monasta L, Montico M, Moradi-Lakeh M, Moran A, Morawska L, Mori R, Murdoch ME, Mwaniki MK, Naidoo K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KMV, Nelson PK, Nelson RG, Nevitt MC, Newton CR, Nolte S, Norman P, Norman R, O'Donnell M, O'Hanlon S, Olives C, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Page A, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Patten SB, Pearce N, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Pesudovs K, Phillips D, Phillips MR, Pierce K, Pion S, Polanczyk GV, Polinder S, Pope CA, Popova S, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Prince M, Pullan RL, Ramaiah KD, Ranganathan D, Razavi H, Regan M, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Richardson K, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Robinson C, De Leòn FR, Ronfani L, Room R, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Saha S, Sampson U, Sanchez-Riera L, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Scott JG, Segui-Gomez M, Shahraz S, Shepard DS, Shin H, Shivakoti R, Singh D, Singh GM, Singh JA, Singleton J, Sleet DA, Sliwa K, Smith E, Smith JL, Stapelberg NJC, Steer A, Steiner T, Stolk WA, Stovner LJ, Sudfeld C, Syed S, Tamburlini G, Tavakkoli M, Taylor HR, Taylor JA, Taylor WJ, Thomas B, Thomson WM, Thurston GD, Tleyjeh IM, Tonelli M, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Tsilimbaris MK, Ubeda C, Undurraga EA, van der Werf MJ, van Os J, Vavilala MS, Venketasubramanian N, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weatherall DJ, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Weisskopf MG, Weissman MM, White RA, Whiteford H, Wiersma ST, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Williams SRM, Witt E, Wolfe F, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh PH, Zaidi AKM, Zheng ZJ, Zonies D, Lopez AD, Murray CJL, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012 Dec 15;380(9859):2163–2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/23245607 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang H, Liu H, Li Z, Zhang K, Wang J, Wang H, Zheng Z. Low back pain associated with lumbar disc herniation: role of moderately degenerative disc and annulus fibrous tears. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Feb 15;8(2):1634–1644. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25932092 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li W, Yang Y, Zhang K, Long E, He L, Zhang L, Zhu Y, Chen C, Liu Z, Wu X, Yun D, Lv J, Liu Y, Liu X, Lin H. Dense anatomical annotation of slit-lamp images improves the performance of deep learning for the diagnosis of ophthalmic disorders. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020 Aug;4(8):767–777. doi: 10.1038/s41551-020-0577-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Zhang K, Liu X, Long E, Jiang J, An Y, Zhang J, Liu Z, Lin Z, Li X, Chen J, Cao Q, Li J, Wu X, Wang D, Li W, Lin H. Comparative analysis of image classification methods for automatic diagnosis of ophthalmic images. Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 31;7:41545. doi: 10.1038/srep41545. doi: 10.1038/srep41545. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Talo M, Baloglu UB, Yıldırım Ö, Rajendra Acharya U. Application of deep transfer learning for automated brain abnormality classification using MR images. Cogn Syst Res. 2019 May;54:176–188. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.12.007. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

