Ultra-high Magnification Endocytoscopy and Molecular Markers for Defining Endoscopic and Histologic Remission in Ulcerative Colitis-An Exploratory Study to Define Deep Remission
- PMID: 34019073
- PMCID: PMC8528147
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izab059
Ultra-high Magnification Endocytoscopy and Molecular Markers for Defining Endoscopic and Histologic Remission in Ulcerative Colitis-An Exploratory Study to Define Deep Remission
Abstract
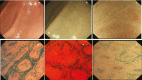
Background: Endoscopic and histological remission are both important treatment goals in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). We aimed to define cellular architecture, expression of molecular markers, and their correlation with endoscopic scores assessed by ultra-high magnification endocytoscopy (ECS) and histological scores.
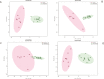
Methods: Patients with UC (n = 29) were prospectively recruited. The correlation among ECS score (ECSS), Mayo endoscopic score (MES), and histological scores were determined. Area under curve were plotted to determine the best thresholds for ECSS that predicted histological remission by Robarts (RHI) and Nancy Histological Index (NHI).Soluble analytes relevant to inflammation were measured in serum and mucosal culture supernatants using ProcartaPlex Luminex assays and studied by partial least square discriminant analysis and logistic model. Mucosal RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were performed to define differentially expressed genes/pathways.
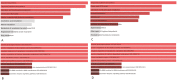
Results: Endocytoscope scoring system correlated strongly with RHI (r = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.51-0.98) and NHI (r = 0.86; 95% CI, 0.42-0.98) but correlated poorly with MES (r = 0.28; 95% CI, 0.27-0.70). We identified soluble brain-derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF), macrophage inflammatory proteins (MIP-1 α) and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (sVCAM-1) predicted histological remission. Mucosal biopsy cultures also identified sVCAM-1 associated with healed mucosa. RNA-seq analysis identified gene expressions shared between ECSS, RHI, or NHI defined healing. A number of gene expressions and pathways were identified including inflammation and metabolic and tumor suppressors that discriminated healed from nonhealed mucosa.
Conclusions: Endocytoscopy represents an interesting tool that may sit between endoscopy and histology-but closer to the latter-identifying gene expression markers and pathways that are also identified by histology.
Keywords: RNA-sequencing; endocytoscope; histological healing; mucosal healing; noninvasive markers.
© 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
Figures



References
-
- Agrawal M, Colombel JF. Treat-to-target in inflammatory bowel diseases, what is the target and how do we treat? Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019;29:421–436. - PubMed
-
- Peyrin-Biroulet L, Sandborn W, Sands BE, et al. Selecting therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease (STRIDE): determining therapeutic goals for treat-to-target. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:1324–1338. - PubMed
-
- Pineton de Chambrun G, Blanc P, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Current evidence supporting mucosal healing and deep remission as important treatment goals for inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;10:915–927. - PubMed
-
- Baert F, Moortgat L, Van Assche G, et al. ; Belgian Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research Group; North-Holland Gut Club . Mucosal healing predicts sustained clinical remission in patients with early-stage Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:463–468; quiz e10. - PubMed
-
- Shah SC, Colombel JF, Sands BE, et al. Mucosal healing is associated with improved long-term outcomes of patients with ulcerative colitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:1245–1255 e1248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

