Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma as a model to understand paracrine and senescence-induced tumourigenesis
- PMID: 34019103
- PMCID: PMC8195904
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-021-03798-7
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma as a model to understand paracrine and senescence-induced tumourigenesis
Abstract
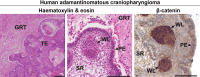
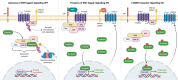
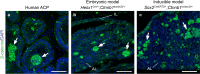
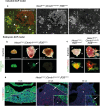
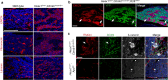
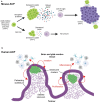
Cellular senescence is a process that can prevent tumour development in a cell autonomous manner by imposing a stable cell cycle arrest after oncogene activation. Paradoxically, senescence can also promote tumour growth cell non-autonomously by creating a permissive tumour microenvironment that fuels tumour initiation, progression to malignancy and metastasis. In a pituitary tumour known as adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma (ACP), cells that carry oncogenic β-catenin mutations and overactivate the WNT signalling pathway form cell clusters that become senescent and activate a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Research in mouse models of ACP has provided insights into the function of the senescent cell clusters and revealed a critical role for SASP-mediated activities in paracrine tumour initiation. In this review, we first discuss this research on ACP and subsequently explore the theme of paracrine tumourigenesis in other tumour models available in the literature. Evidence is accumulating supporting the notion that paracrine signalling brought about by senescent cells may underlie tumourigenesis across different tumours and cancer models.
Keywords: Cancer stem cells; Oncogene-induced senescence; Pituitary tumour; SOX2; Senolytics; Therapy-induced senescence; WNT/β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

