Antibodies against human endogenous retrovirus K102 envelope activate neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 34019642
- PMCID: PMC8144942
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20191766
Antibodies against human endogenous retrovirus K102 envelope activate neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
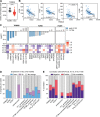
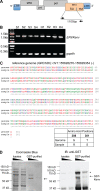
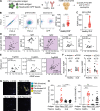
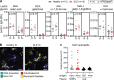
Neutrophil activation and the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are hallmarks of innate immune activation in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Here we report that the expression of an endogenous retrovirus (ERV) locus ERV-K102, encoding an envelope protein, was significantly elevated in SLE patient blood and correlated with autoantibody levels and higher interferon status. Induction of ERV-K102 in SLE negatively correlated with the expression of epigenetic silencing factors. Anti-ERV-K102 IgG levels in SLE plasma correlated with higher interferon stimulated gene expression, and further promoted enhanced neutrophil phagocytosis of ERV-K102 envelope protein through immune complex formation. Finally, phagocytosis of ERV-K102 immune complexes resulted in the formation of NETs consisting of DNA, neutrophil elastase, and citrullinated histone H3. Together, we identified an immunostimulatory ERV-K envelope protein that in an immune complex with SLE IgG is capable of activating neutrophils.
© 2021 Tokuyama et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: M.J. Townsend reported "other" from Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, outside the submitted work. G. Alter reported "other" from Seromyx Systems Inc. and grants from Pfizer, GSK, BMS, Merck, Gilead, Novavax, Janssen, Sanofi outside the submitted work; in addition, G. Alter had a patent to Systems Serology Platform pending. A. Iwasaki reported grants from AbbVie during the conduct of the study; "other" from RIGImmune; and personal fees from InProTher and Boehringer Ingelheim outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures






References
-
- Absher, D.M., Li X., Waite L.L., Gibson A., Roberts K., Edberg J., Chatham W.W., and Kimberly R.P.. 2013. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus reveals persistent hypomethylation of interferon genes and compositional changes to CD4+ T-cell populations. PLoS Genet. 9:e1003678. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003678 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrews, B.S., Eisenberg R.A., Theofilopoulos A.N., Izui S., Wilson C.B., McConahey P.J., Murphy E.D., Roths J.B., and Dixon F.J.. 1978. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J. Exp. Med. 148:1198–1215. 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banki, K., Maceda J., Hurley E., Ablonczy E., Mattson D.H., Szegedy L., Hung C., and Perl A.. 1992. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV)-related endogenous sequence, HRES-1, encodes a 28-kDa protein: a possible autoantigen for HTLV-I gag-reactive autoantibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89:1939–1943. 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1939 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

